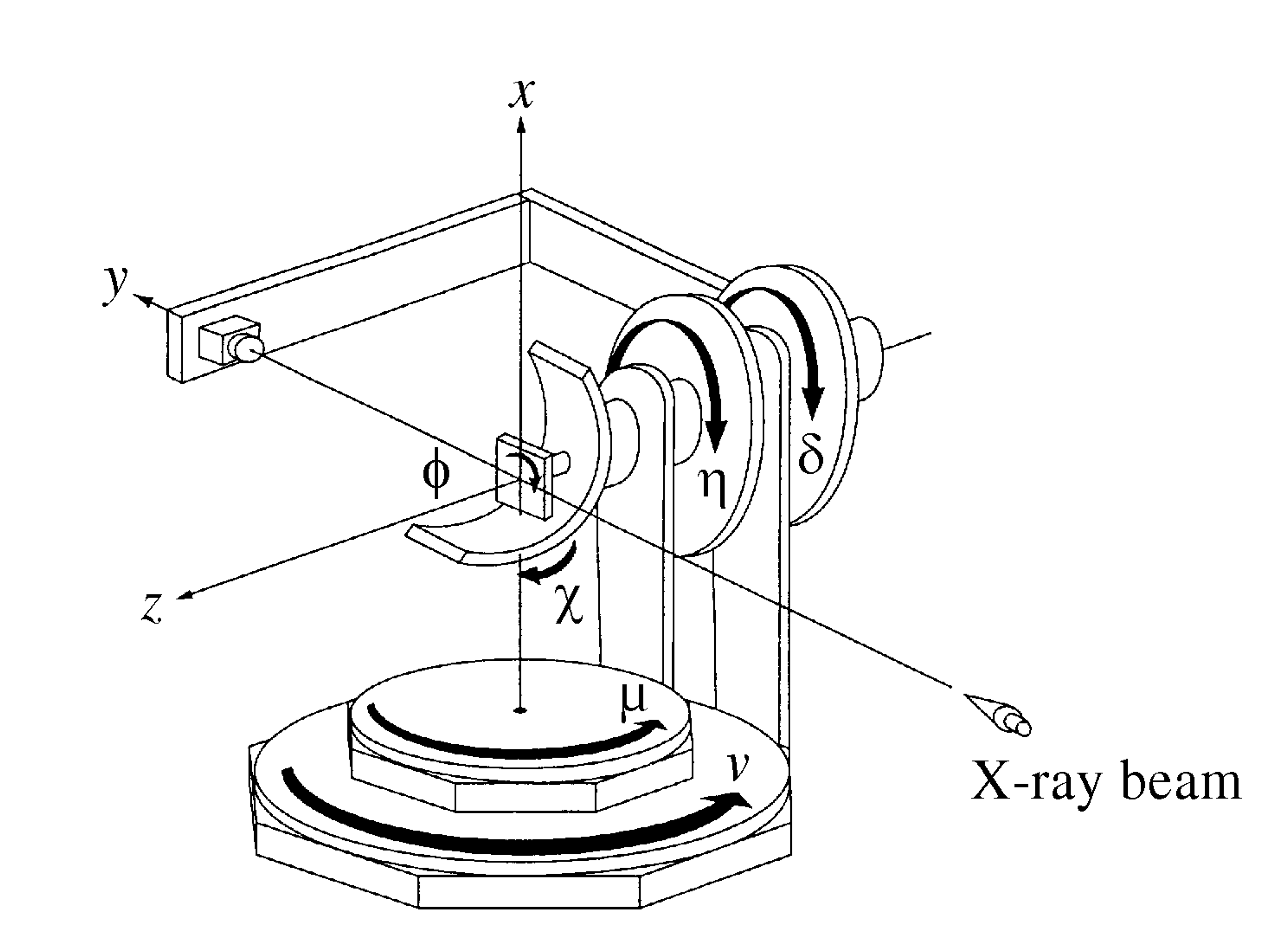
Diffcalc is a python/jython based diffraction condition calculator used for controlling diffractometers within reciprocal lattice space. It performs the same task as the fourc, sixc, twoc, kappa, psic and surf macros from SPEC.
There is a user guide and developer guide, both at diffcalc.readthedocs.io
IMPORTANT: Python 3 version of diffcalc calculator code is available as diffcalc-core project https://github.com/DiamondLightSource/diffcalc-core/
- Written in Python using numpy
- Works in Jython using Jama
- Runs directly in OpenGDA<http://www.opengda.org>
- Runs in in Python or IPython using minimal OpenGda emulation (included)
- Contact us for help running in your environment
Diffcalc’s standard calculation engine is an implementation of [You1999] and [Busing1967]. Diffcalc works with any diffractometer which is a subset of:
Diffcalc can be configured to work with any diffractometer geometry which is a subset of this. For example, a five-circle diffractometer might be missing the nu circle above.
Note that the first versions of Diffcalc were based on [Vlieg1993] and [Vlieg1998] and a ‘Vlieg’ engine is still available. There is also an engine based on [Willmott2011]. The ‘You’ engine is more generic and the plan is to remove the old ‘Vlieg’ engine once beamlines have been migrated.
Check it out:
$ git clone https://github.com/DiamondLightSource/diffcalc.git
Cloning into 'diffcalc'...At Diamond Diffcalc may be installed within an OpenGDA deployment and is available via the 'module' system from bash.
Start diffcalc in ipython using a sixcircle dummy diffractometer:
$ cd diffcalc
$ ./diffcalc.py --help
...
$ ./diffcalc.py sixcircle
Running: "ipython --no-banner --HistoryManager.hist_file=/tmp/ipython_hist_zrb13439.sqlite -i -m diffcmd.start sixcircle False"
---------------------------------- DIFFCALC -----------------------------------
Startup script: '/Users/zrb13439/git/diffcalc/startup/sixcircle.py'
Loading ub calculation: 'test'
------------------------------------ Help -------------------------------------
Quick: https://github.com/DiamondLightSource/diffcalc/blob/master/README.rst
Manual: https://diffcalc.readthedocs.io
Type: > help ub
> help hkl
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
In [1]:Within Diamond use:
$ module load diffcalc
$ diffcalc --help
...
$ diffcalc sixcircleType demo.all() to see it working and then move try the following quick start guide:
>>> demo.all()
...To view help with orientation and then moving in hkl space:
>>> help ub
...
>>> help hkl
...See the full user manual<https://diffcalc.readthedocs.io> for many more options and an explanation of what this all means.
To load the last used UB-calculation:
>>> lastub
Loading ub calculation: 'mono-Si'To load a previous UB-calculation:
>>> listub
UB calculations in: /Users/walton/.diffcalc/i16
0) mono-Si 15 Feb 2017 (22:32)
1) i16-32 13 Feb 2017 (18:32)
>>> loadub 0To create a new UB-calculation:
>>> newub 'example'
>>> setlat '1Acube' 1 1 1 90 90 90Find U matrix from two reflections:
>>> pos wl 1
wl: 1.0000
>>> c2th [0 0 1]
59.99999999999999
>>> pos sixc [0 60 0 30 90 0]
sixc: mu: 0.0000 delta: 60.0000 gam: 0.0000 eta: 30.0000 chi: 90.0000 phi: 0.0000
>>> addref [0 0 1]
>>> pos sixc [0 90 0 45 45 90]
sixc: mu: 0.0000 delta: 90.0000 gam: 0.0000 eta: 45.0000 chi: 45.0000 phi: 90.0000
>>> addref [0 1 1]
Calculating UB matrix.Check that it looks good:
>>> checkub
ENERGY H K L H_COMP K_COMP L_COMP TAG
1 12.3984 0.00 0.00 1.00 0.0000 0.0000 1.0000
2 12.3984 0.00 1.00 1.00 0.0000 1.0000 1.0000 To see the resulting UB-calculation:
>>> ub
UBCALC
name: example
n_phi: 0.00000 0.00000 1.00000 <- set
n_hkl: -0.00000 0.00000 1.00000
miscut: None
CRYSTAL
name: 1Acube
a, b, c: 1.00000 1.00000 1.00000
90.00000 90.00000 90.00000
B matrix: 6.28319 0.00000 0.00000
0.00000 6.28319 0.00000
0.00000 0.00000 6.28319
UB MATRIX
U matrix: 1.00000 0.00000 0.00000
0.00000 1.00000 0.00000
0.00000 0.00000 1.00000
U angle: 0
UB matrix: 6.28319 0.00000 0.00000
0.00000 6.28319 0.00000
0.00000 0.00000 6.28319
REFLECTIONS
ENERGY H K L MU DELTA GAM ETA CHI PHI TAG
1 12.398 0.00 0.00 1.00 0.0000 60.0000 0.0000 30.0000 90.0000 0.0000
2 12.398 0.00 1.00 1.00 0.0000 90.0000 0.0000 45.0000 45.0000 90.0000 See the full user manual<https://diffcalc.readthedocs.io> for many more options and an explanation of what this all means.
By default the reference vector is set parallel to the phi axis. That is, along the z-axis of the phi coordinate frame.
The ub command shows the current reference vector, along with any inferred miscut, at the top its report (or it can be shown by calling setnphi or setnhkl' with no args):
>>> ub
...
n_phi: 0.00000 0.00000 1.00000 <- set
n_hkl: -0.00000 0.00000 1.00000
miscut: None
...See the full user manual<https://diffcalc.readthedocs.io> for many more options and an explanation of what this all means.
To get help and see current constraints:
>>> help con
...
>>> con
DET REF SAMP
------ ------ ------
delta --> a_eq_b --> mu
--> gam alpha eta
qaz beta chi
naz psi phi
mu_is_gam
gam : 0.0000
a_eq_b
mu : 0.0000
Type 'help con' for instructionsThree constraints can be given: zero or one from the DET and REF columns and the remainder from the SAMP column. Not all combinations are currently available. Use help con to see a summary if you run into troubles.
To configure four-circle vertical scattering:
>>> con gam 0 mu 0 a_eq_b
gam : 0.0000
a_eq_b
mu : 0.0000Simulate moving to a reflection:
>>> sim hkl [0 1 1]
sixc would move to:
mu : 0.0000
delta : 90.0000
gam : 0.0000
eta : 45.0000
chi : 45.0000
phi : 90.0000
alpha : 30.0000
beta : 30.0000
naz : 35.2644
psi : 90.0000
qaz : 90.0000
tau : 45.0000
theta : 45.0000Move to reflection:
>>> pos hkl [0 1 1]
hkl: h: 0.00000 k: 1.00000 l: 1.00000
>>> pos sixc
sixc: mu: 0.0000 delta: 90.0000 gam: 0.0000 eta: 45.0000 chi: 45.0000 phi: 90.0000 Scan an hkl axis (and read back settings):
>>> scan l 0 1 .2 sixc
l mu delta gam eta chi phi
------- ------- -------- ------- -------- ------- --------
0.00000 0.0000 60.0000 0.0000 30.0000 0.0000 90.0000
0.20000 0.0000 61.3146 0.0000 30.6573 11.3099 90.0000
0.40000 0.0000 65.1654 0.0000 32.5827 21.8014 90.0000
0.60000 0.0000 71.3371 0.0000 35.6685 30.9638 90.0000
0.80000 0.0000 79.6302 0.0000 39.8151 38.6598 90.0000
1.00000 0.0000 90.0000 0.0000 45.0000 45.0000 90.0000Scan a constraint (and read back virtual angles and eta):
>>> con psi
gam : 0.0000
! psi : ---
mu : 0.0000
>>> scan psi 70 110 10 hklverbose [0 1 1] eta
psi eta h k l theta qaz alpha naz tau psi beta
-------- -------- ------- ------- ------- -------- -------- -------- -------- -------- -------- --------
70.00000 26.1183 0.00000 1.00000 1.00000 45.00000 90.00000 19.20748 45.28089 45.00000 70.00000 42.14507
80.00000 35.1489 -0.00000 1.00000 1.00000 45.00000 90.00000 24.40450 40.12074 45.00000 80.00000 35.93196
90.00000 45.0000 0.00000 1.00000 1.00000 45.00000 90.00000 30.00000 35.26439 45.00000 90.00000 30.00000
100.00000 54.8511 -0.00000 1.00000 1.00000 45.00000 90.00000 35.93196 30.68206 45.00000 100.00000 24.40450
110.00000 63.8817 -0.00000 1.00000 1.00000 45.00000 90.00000 42.14507 26.34100 45.00000 110.00000 19.20748| STATE | |
| -- newub {'name'} | start a new ub calculation name |
| -- loadub 'name' | num | load an existing ub calculation |
| -- lastub | load the last used ub calculation |
| -- listub | list the ub calculations available to load |
| -- rmub 'name'|num | remove existing ub calculation |
| -- saveubas 'name' | save the ub calculation with a new name |
| LATTICE | |
| -- setlat | interactively enter lattice parameters (Angstroms and Deg) |
| -- setlat name a | assumes cubic |
| -- setlat name a b | assumes tetragonal |
| -- setlat name a b c | assumes ortho |
| -- setlat name a b c gamma | assumes mon/hex with gam not equal to 90 |
| -- setlat name a b c alpha beta gamma | arbitrary |
| -- c2th [h k l] | calculate two-theta angle for reflection |
| -- hklangle [h1 k1 l1] [h2 k2 l2] | calculate angle between [h1 k1 l1] and [h2 k2 l2] crystal planes |
| REFERENCE (SURFACE) | |
| -- setnphi {[x y z]} | sets or displays n_phi reference |
| -- setnhkl {[h k l]} | sets or displays n_hkl reference |
| REFLECTIONS | |
| -- showref | shows full reflection list |
| -- addref | add reflection interactively |
| -- addref [h k l] {'tag'} | add reflection with current position and energy |
| -- addref [h k l] (p1, .., pN) energy {'tag'} | add arbitrary reflection |
| -- editref num | interactively edit a reflection |
| -- delref num | deletes a reflection (numbered from 1) |
| -- clearref | deletes all the reflections |
| -- swapref | swaps first two reflections used for calculating U matrix |
| -- swapref num1 num2 | swaps two reflections (numbered from 1) |
| CRYSTAL ORIENTATIONS | |
| -- showorient | shows full list of crystal orientations |
| -- addorient | add crystal orientation interactively |
| -- addorient [h k l] [x y z] {'tag'} | add crystal orientation in laboratory frame |
| -- editorient num | interactively edit a crystal orientation |
| -- delorient num | deletes a crystal orientation (numbered from 1) |
| -- clearorient | deletes all the crystal orientations |
| -- swaporient | swaps first two crystal orientations used for calculating U matrix |
| -- swaporient num1 num2 | swaps two crystal orientations (numbered from 1) |
| UB MATRIX | |
| -- checkub | show calculated and entered hkl values for reflections |
| -- setu {[[..][..][..]]} | manually set u matrix |
| -- setub {[[..][..][..]]} | manually set ub matrix |
| -- calcub | (re)calculate u matrix from ref1 and ref2 |
| -- trialub | (re)calculate u matrix from ref1 only (check carefully) |
| -- refineub {[h k l]} {pos} | refine unit cell dimensions and U matrix to match diffractometer angles for a given hkl value |
| -- addmiscut angle {[x y z]} | apply miscut to U matrix using a specified miscut angle in degrees and a rotation axis (default: [0 1 0]) |
| -- setmiscut angle {[x y z]} | manually set U matrix using a specified miscut angle in degrees and a rotation axis (default: [0 1 0]) |
| CONSTRAINTS | |
| -- con | list available constraints and values |
| -- con <name> {val} | constrains and optionally sets one constraint |
| -- con <name> {val} <name> {val} <name> {val} | clears and then fully constrains |
| -- uncon <name> | remove constraint |
| HKL | |
| -- allhkl [h k l] | print all hkl solutions ignoring limits |
| HARDWARE | |
| -- hardware | show diffcalc limits and cuts |
| -- setcut {name {val}} | sets cut angle |
| -- setmin {axis {val}} | set lower limits used by auto sector code (None to clear) |
| -- setmax {name {val}} | sets upper limits used by auto sector code (None to clear) |
| MOTION | |
| -- sim hkl scn | simulates moving scannable (not all) |
| -- sixc | show Eularian position |
| -- pos sixc [mu, delta, gam, eta, chi, phi] | move to Eularian position(None holds an axis still) |
| -- sim sixc [mu, delta, gam, eta, chi, phi] | simulate move to Eulerian positionsixc |
| -- hkl | show hkl position |
| -- pos hkl [h k l] | move to hkl position |
| -- pos {h | k | l} val | move h, k or l to val |
| -- sim hkl [h k l] | simulate move to hkl position |
- Busing1967
W. R. Busing and H. A. Levy. Angle calculations for 3- and 4-circle X-ray and neutron diffractometers. Acta Cryst. (1967). 22, 457-464. (pdf link).
- Vlieg1993
Martin Lohmeier and Elias Vlieg. Angle calculations for a six-circle surface x-ray diffractometer. J. Appl. Cryst. (1993). 26, 706-716. (pdf link).
- Vlieg1998
Elias Vlieg. A (2+3)-type surface diffractometer: mergence of the z-axis and (2+2)-type geometries. J. Appl. Cryst. (1998). 31, 198-203. (pdf link).
- Willmott2011
- Schlepütz, S. O. Mariager, S. A. Pauli, R. Feidenhans'l and
P. R. Willmott. Angle calculations for a (2+3)-type diffractometer: focus on area detectors. J. Appl. Cryst. (2011). 44, 73-83. (pdf link).
- You1999
- You. Angle calculations for a '4S+2D' six-circle diffractometer.
J. Appl. Cryst. (1999). 32, 614-623. (pdf link).