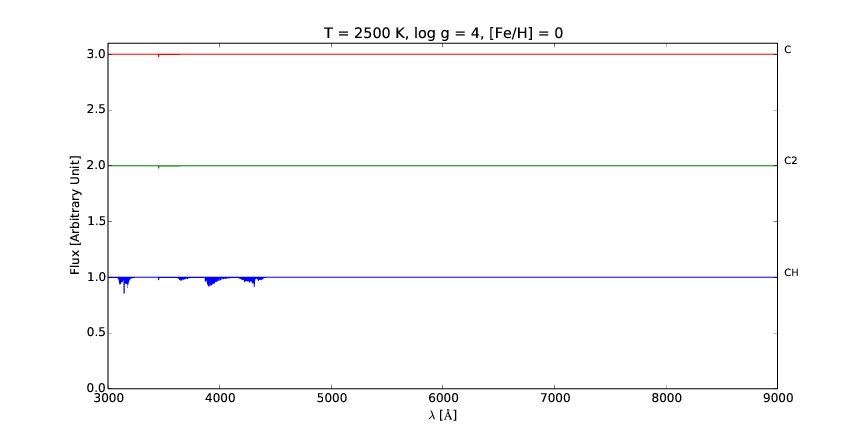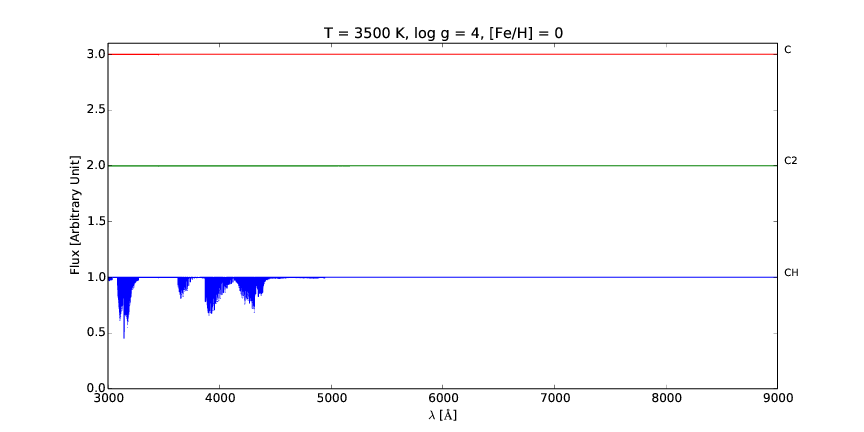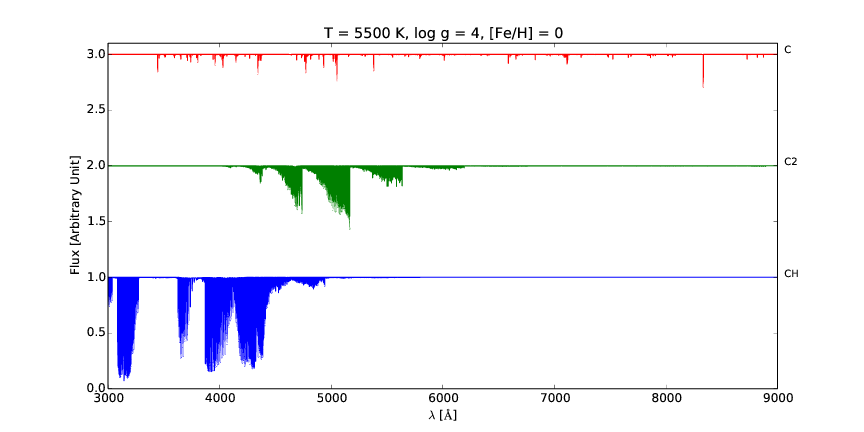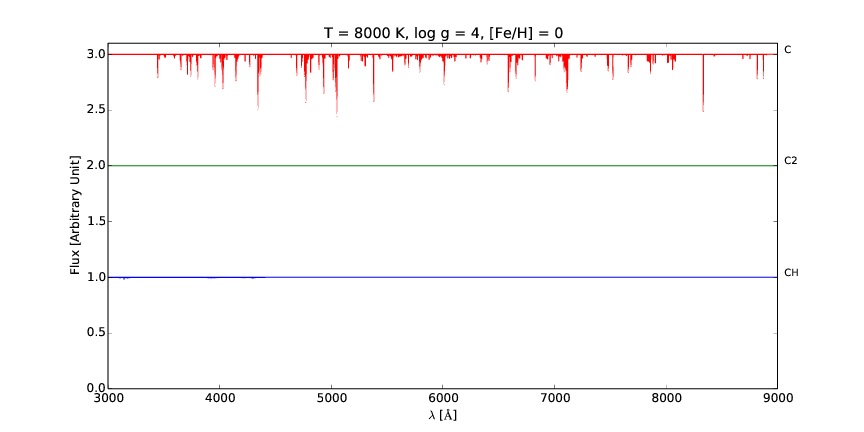
pspec is a versatile line command tool for interactive plotting and comparison of stellar spectra.
To get help on line command arguments, type pspec.py -h
Write an output plot in plot.png (see -o option for specifying name and extension [eps|pdf|png])
Main options for comparison are:
- constant or linear normalization
- smoothing
- vertical shifting individually or per group
- line identification (to improve)
- wavelength correction
- save plots in pdf, eps or png
- save normalized and/or smoothed spectra in ASCII
- in: input test stellar spectra with different formats
- bs: benchmark stars - optical spectra of the Sun and Arcturus in binary format
- ll: linelists - list of lines for visual identification
- Fraunhofer lines,
- solar lines (Moore 1966),
- stellar lines (Coluzzi 1993),
- stellar lines only with stellar type (Coluzzi 1993),
- molecular lines (Turnshek 1985, based on cool K and M stars)
- VALD (exhaustive linelist, not very useful for the moment)
pspec.py - python 2.7 tool to plot spectra based on matplotlib graphic library modules required:
- in standard library: os, struct, argparse
- not in standard library: pylab and pyfits
This is main advantage of pspec: the input is versatile. It can be:
- a spectrum
- a list of spectra
- a file containing path and name of one or several spectra
- a list of files
- a combination of spectra and files
Spectra can be either in ASCII, FITS or binary (little-endian) format.
Format is basically two columns with wavelengths (in Å but can manage also nm) and flux.
Default name of input file is speclist.txt
If pspec is run without name of spectrum or input filename,
it is speclist.txt which is read.
The default configuration is defined in the __main__ of python program pspec.py.
- Default input filename:
speclist.txt - Default central wavelength: 6569.214 Å (Fe I line in the red wing of Halpha)
- Default wavelength range: 20.001 Å
- Default border width for broadening: 3.0 Å
- Default linelist for wavelength range larger than 600 Å: '/home/tmerle/dev/pspec/ll/ll_franhofer.dat'
- Default linelist for wavelength range lower than 600 Å: '/home/tmerle/dev/pspec/ll/ll_moore.dat'
Warning: change the linelist paths according to your file tree.
-
The simplest way is:
$ pspecThis will try to find a input file name
speclist.txtand display the spectra with their specifications. -
The secund simplest way is:
$ pspec path\_and\_name\_of\_your\_spectrumE.g:
$ pspec bs/sun_kpno.binThis will display the spectrum over its entire wavenlength range
-
Imagine that you have 3 observed spectra (
spec1.fits,spec2.fitsandspec3.fits) that you want to visually inspect between 5160 and 5190 Å with line identification.$ pspec spec1.fits spec2.fits spec3.fits -wmin 5160 -wmax 5190 -nn -vs 1 -lwhich is strictly equivalent to:
$ pspec spec1.fits spec2.fits spec3.fits -w 5175 -r 30 -nn -vs 1 -l-wminand-wmaxoptions are the min and the max wavelength range in Å and these options are strictly equivant to give the central wavelength (-w) and the range (-r)-ndoes constant normalization whereas -nn does linear normalization-vs1 says that the spectra has to be shift vertically by arbitray unit of one-lsays to add a default linelist identification to the plot but you can specify an other file -
Imagine that you want to compare a theoretical spectrum with observation (i.e. stacked) and you want to add over that a benchmark spectrum for comparison. You want to smooth the theoretical one at 6 km/s to stick to the resolution of the observed spectrum.
Your input file could be as:
# Path and name of spectra | Legend |unit|sym| shift | save | broadening | group | absolute legend position in/test.bin |theo | | | | | 6 | 1 | 0.9 in/test.fit |obs | | | | | | 1 | 1.1 bs/sun_kpno.bin | Sun | | | | | | 2 |The line command could be as:
$ pspec -w 8498 -r 20 -nn -l -vs 1
-
Link it in e.g. $HOME/bin:
$ ln -s pspec.py $HOME/bin -
create an alias in your hidden configuration file
For bash shell in .bashrc:alias pspec=/home/tmerle/dev/pspec/pspec.pyFor tcsh shell in .tcshrc:
alias pspec '/home/tmerle/dev/pspec/pspec.py'
The simplest way to do is to set one path and spectrum name per entries.
You do NOT have to use quotes since all parameters are read as strings.
e.g:
$ cat my_speclist.txt
bs/sun_kpno.bin
bs/arcturus_hermes.bi
...
Then you can specified 9 parameters per entries. The field separator is |.
The order of the parameters matters.
- The legend for the spectrum
- The unit of wavelength: in Angström [Å|A|a] or in nanometer [nm] (Default)
- The symbol used for plotting spectrum (e.g. '
r+' for red line with plusses, 'k-' for black line,...) - The wavelength shift in Å (only useful for plotting a specific line, to improve for radial velocity correction)
- Save option (True|False): post-processed spectrum in written in ASCII format
- Individual broadening parameter (dispersion in km/s): without effect if the line command option
-bis used - The group option: integer which specifies at which group among a spectrum (useful with
-vsline command argument) - The absolute legend position in ordinate coordinate level
- Individual normalization parameter (1 or 2 for constant/linear normalization): without effect if the command line option
-nor-nnis used
You can comment a line using # character.
All parameters are optional.
If you need the 3rd parameter just let field empty not forgetting field separator.
E.g:
$ cat speclist.txt
bs/sun_kpno.bin | | |'r-'|
Default options:
- legend: None
- unit of wavelenght: Å
- symbol: matplotlib default
- wavelength shift: 0 Å
- save: False
- broadening: 0 km/s
- group option: None
- absolute legend position: None
An example of an extensive input file:
$ cat speclist.txt
# Path and name of spectra | Legend |unit|sym|shift|save| broadening |group| absolute legend position | normalization
bs/sun_kpno.bin | Sun | |r- | |True| 6 | |
bs/arcturus_hermes.bin |Arcturus| |b- |-0.2 | | | |
Please send an email to thibault@merle.fr for any comments or bugs to fix.
gir_19235180+0048006_H875.7.fit from GES DR1 => test.fit, test.dat, test.bin