You can use ropper to display information about binary files in different file formats and you can search for gadgets to build rop chains for different architectures (x86/X86_64, ARM/ARM64, MIPS/MIPS64, PowerPC). For disassembly ropper uses the awesome Capstone Framework.
NOTE: I recommend to use the dev version of ropper, because bugfixes are earlier available in dev branch.
Install Capstone with PyPi:
$ sudo pip install capstone
Install filebytes with PyPi:
$ sudo pip install filebytes
Optional (not needed to run ropper just to look for gadgets):
Install Keystone:
You will find the command here, as soon as keystone is released.
Install and execute Ropper
$ python setup.py install
$ ropper
You can also install Ropper with pip
$ pip install ropper
If you want, you can use Ropper without installation
$ ./Ropper.py
If you don't want to install filebytes, filebytes is a submodule of the ropper repository. This means you don't need to install filebytes and ropper.
$ git clone https://github.com/sashs/ropper.git
$ cd ropper
$ git submodule init
$ git submodule update
$ ./Ropper.py
usage: Ropper.py [-h] [-v] [--console] [-f <file>] [-r] [--db <dbfile>]
[-a <arch>] [--section <section>] [--string [<string>]]
[--hex] [--asm <asm> [H|S|R] [<asm> [H|S|R] ...]]
[--disasm <opcode>] [--disassemble-address <address:length>]
[-i] [-e] [--imagebase] [-c] [-s] [-S] [--imports]
[--symbols] [--set <option>] [--unset <option>]
[-I <imagebase>] [-p] [-j <reg>] [--stack-pivot]
[--inst-count <n bytes>] [--search <regex>]
[--quality <quality>] [--filter <regex>] [--opcode <opcode>]
[--instructions <instructions>] [--type <type>] [--detailed]
[--all] [--chain <generator>] [-b <badbytes>] [--nocolor]
You can use ropper to display information about binary files in different file formats
and you can search for gadgets to build rop chains for different architectures
supported filetypes:
ELF
PE
Mach-O
Raw
supported architectures:
x86 [x86]
x86_64 [x86_64]
MIPS [MIPS, MIPS64]
ARM/Thumb [ARM, ARMTHUMB]
ARM64 [ARM64]
PowerPC [PPC, PPC64]
available rop chain generators:
execve (execve[=<cmd>], default /bin/sh) [Linux x86, x86_64]
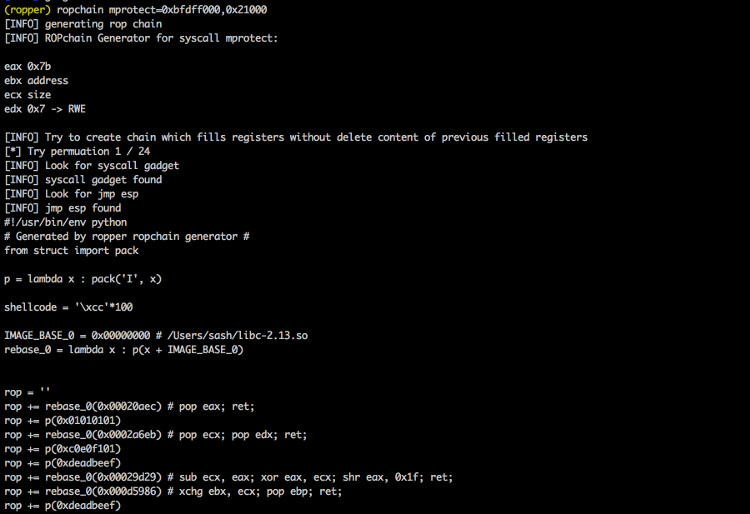
mprotect (mprotect=<address>:<size>) [Linux x86, x86_64]
virtualprotect (virtualprotect=<address iat vp>:<size>) [Windows x86]
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-v, --version Print version
--console Starts interactive commandline
-f <file>, --file <file>
The file to load
-r, --raw Loads the file as raw file
--db <dbfile> The dbfile to load
-a <arch>, --arch <arch>
The architecture of the loaded file
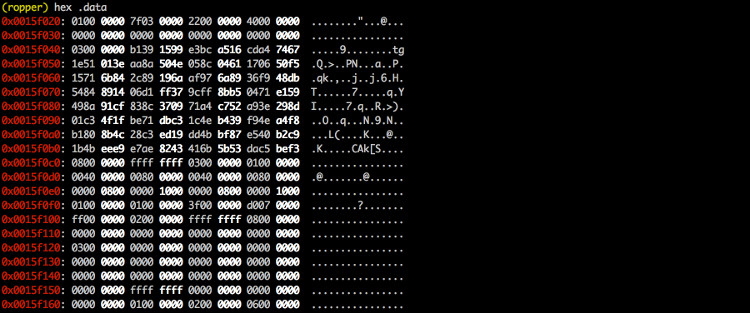
--section <section> The data of the this section should be printed
--string [<string>] Looks for the string <string> in all data sections
--hex Prints the selected sections in a hex format
--asm <asm> [H|S|R] [<asm> [H|S|R] ...]
A string to assemble and a format of the output
(H=HEX, S=STRING, R=RAW, default: H)
--disasm <opcode> Opcode to disassemble (e.g. ffe4, 89c8c3, ...)
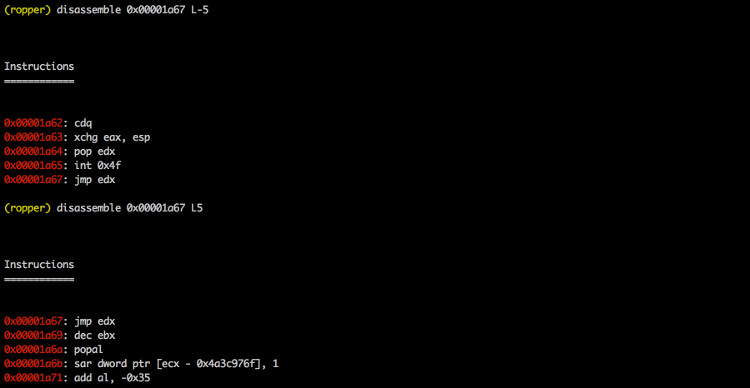
--disassemble-address <address:length>
Disassembles instruction at address <address>
(0x12345678:L3). The count of instructions to
disassemble can be specified (0x....:L...)
-i, --info Shows file header [ELF/PE/Mach-O]
-e Shows EntryPoint
--imagebase Shows ImageBase [ELF/PE/Mach-O]
-c, --dllcharacteristics
Shows DllCharacteristics [PE]
-s, --sections Shows file sections [ELF/PE/Mach-O]
-S, --segments Shows file segments [ELF/Mach-O]
--imports Shows imports [ELF/PE]
--symbols Shows symbols [ELF]
--set <option> Sets options. Available options: aslr nx
--unset <option> Unsets options. Available options: aslr nx
-I <imagebase> Uses this imagebase for gadgets
-p, --ppr Searches for 'pop reg; pop reg; ret' instructions
[only x86/x86_64]
-j <reg>, --jmp <reg>
Searches for 'jmp reg' instructions (-j reg[,reg...])
[only x86/x86_64]
--stack-pivot Prints all stack pivot gadgets
--inst-count <n bytes>
Specifies the max count of instructions in a gadget
(default: 6)
--search <regex> Searches for gadgets
--quality <quality> The quality for gadgets which are found by search (1 =
best)
--filter <regex> Filters gadgets
--opcode <opcode> Searchs for opcodes (e.g. ffe4 or ffe? or ff??)
--instructions <instructions>
Searchs for instructions (e.g. "jmp esp", "pop eax;
ret")
--type <type> Sets the type of gadgets [rop, jop, sys, all]
(default: all)
--detailed Prints gadgets more detailed
--all Does not remove duplicate gadgets
--chain <generator> Generates a ropchain [generator=parameter]
-b <badbytes>, --badbytes <badbytes>
Set bytes which should not contains in gadgets
--nocolor Disables colored output
example uses:
[Generic]
ropper.py
ropper.py --file /bin/ls --console
[Informations]
Ropper.py --file /bin/ls --info
Ropper.py --file /bin/ls --imports
Ropper.py --file /bin/ls --sections
Ropper.py --file /bin/ls --segments
Ropper.py --file /bin/ls --set nx
Ropper.py --file /bin/ls --unset nx
[Gadgets]
Ropper.py --file /bin/ls --inst-count 5
Ropper.py --file /bin/ls --search "sub eax" --badbytes 000a0d
Ropper.py --file /bin/ls --search "sub eax" --detail
Ropper.py --file /bin/ls --filter "sub eax"
Ropper.py --file /bin/ls --inst-count 5 --filter "sub eax"
Ropper.py --file /bin/ls --opcode ffe4
Ropper.py --file /bin/ls --opcode ffe?
Ropper.py --file /bin/ls --opcode ??e4
Ropper.py --file /bin/ls --detailed
Ropper.py --file /bin/ls --ppr --nocolor
Ropper.py --file /bin/ls --jmp esp,eax
Ropper.py --file /bin/ls --type jop
Ropper.py --file /bin/ls --chain execve
Ropper.py --file /bin/ls --chain execve=/bin/sh
Ropper.py --file /bin/ls --chain execve=/bin/sh --badbytes 000a0d
Ropper.py --file /bin/ls --chain mprotect=0xbfdff000:0x21000
[Assemble/Disassemble]
Ropper.py --asm "jmp esp"
Ropper.py --asm "mov eax, ecx; ret"
Ropper.py --disasm ffe4
[Search]
Ropper.py --file /bin/ls --search <searchstring>
? any character
% any string
Example:
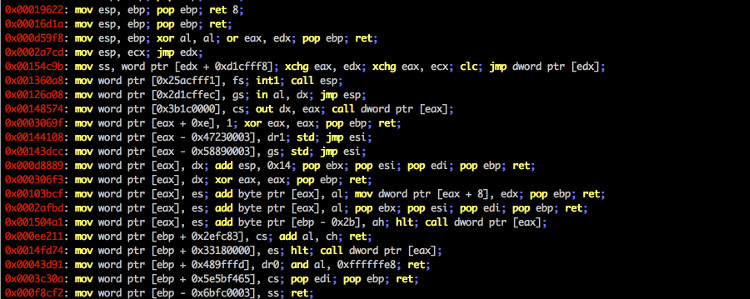
ropper.py --file /bin/ls --search "mov e?x"
0x000067f1: mov edx, dword ptr [ebp + 0x14]; mov dword ptr [esp], edx; call eax
0x00006d03: mov eax, esi; pop ebx; pop esi; pop edi; pop ebp; ret ;
0x00006d6f: mov ebx, esi; mov esi, dword ptr [esp + 0x18]; add esp, 0x1c; ret ;
0x000076f8: mov eax, dword ptr [eax]; mov byte ptr [eax + edx], 0; add esp, 0x18; pop ebx; ret ;
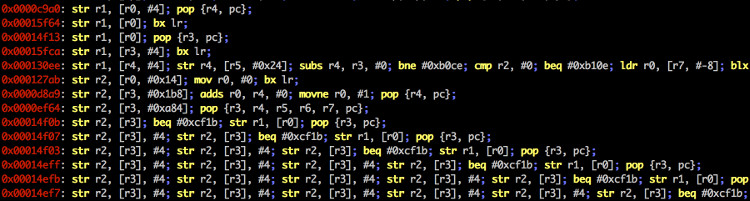
ropper.py --file /bin/ls --search "mov [%], edx"
0x000067ed: mov dword ptr [esp + 4], edx; mov edx, dword ptr [ebp + 0x14]; mov dword ptr [esp], edx; call eax;
0x00006f4e: mov dword ptr [ecx + 0x14], edx; add esp, 0x2c; pop ebx; pop esi; pop edi; pop ebp; ret ;
0x000084b8: mov dword ptr [eax], edx; ret ;
0x00008d9b: mov dword ptr [eax], edx; add esp, 0x18; pop ebx; ret ;
ropper.py --file /bin/ls --search "mov [%], edx" --quality 1
0x000084b8: mov dword ptr [eax], edx; ret ;
from ropper import *
##### open a binary ######
binary_elf = Loader.open('test-binaries/ls-x86')
# binary_elf = elf.ELF('test-binaries/ls-x86')
binary_pe = Loader.open('test-binaries/cmd-x86.exe')
# binary_pe = pe.PE('test-binaries/cmd-x86.exe')
binary_macho = Loader.open('test-binaries/ls-macho-x86_64')
# binary_macho = mach_o.MachO('test-binaries/ls-macho-x86_64')
binary_raw = Loader.open('test-binaries/ls-x86', raw=True, arch=x86) # x86, x86_64, ARM, ARMTHUMB, ARM64, PPC, PPC64, MIPS, MIPS64
print binary_elf.type == Type.ELF
print binary_pe.type == Type.PE
print binary_macho.type == Type.MACH_O
print binary_raw.type == Type.RAW
# Set architecture of a binary, so it is possible to look for gadgets for a different architecture
# It is useful for ARM if you want to look for ARM gadgets or Thumb gadgets
# Or if you opened a raw file
binary_elf.arch = x86
binary_elf.arch = x86_64
binary_elf.arch = ARM
binary_elf.arch = ARMTHUMB
binary_elf.arch = ARM64
binary_elf.arch = MIPS
binary_elf.arch = MIPS64
binary_elf.arch = PPC
binary_elf.arch = PPC64
binary_elf.arch = x86
##### load gadgets ######
rop = Ropper()
gadgets = rop.searchGadgets(binary_elf)
gadgets = rop.searchGadgets(binary_elf, gtype=GadgetType.JOP)
gadgets = rop.searchGadgets(binary_pe, gtype=GadgetType.ROP)
gadgets = rop.searchGadgets(binary_elf, instructionCount=5)
##### search pop pop ret ######
pprs = rop.searchPopPopRet(binary_elf)
##### load jmp reg ######
jmp_regs = rop.searchJmpReg(binary_pe, ['esp', 'eax'])
##### search opcode ######
opcode_gadgets = rop.searchOpcode(binary_elf, 'ffe4')
opcode_gadgets = rop.searchOpcode(binary_elf, 'ffe?')
opcode_gadgets = rop.searchOpcode(binary_elf, '??e4')
##### search instructions ######
opcode_gadgets = rop.searchInstructions(binary_elf, 'jmp esp')
opcode_gadgets = rop.searchInstructions(binary_elf, 'pop eax; ret')
##### assemble instructions ######
hex_string = rop.assemble('jmp esp')
print '"jmp esp" assembled to hex string =', hex_string
raw_bytes = rop.assemble('jmp esp', format=FORMAT.RAW)
print '"jmp esp" assembled to raw bytes =', raw_bytes
string = rop.assemble('jmp esp', format=FORMAT.STRING)
print '"jmp esp" assembled to string =',string
arm_bytes = rop.assemble('bx sp', arch=ARM)
print '"bx sp" assembled to hex string =', arm_bytes
##### disassemble bytes #######
arm_instructions = rop.disassemble(arm_bytes, arch=ARM)
print arm_bytes, 'disassembled to "%s"' % arm_instructions
# Change the imagebase, this also change the imagebase for all loaded gadgets of this binary
binary_elf.imageBase = 0x0
# reset image base
binary_elf.imageBase = None
# print a gadget
print gadgets[0]
# print simple
print gadgets[0].simpleString()
# gadget address
print hex(gadgets[0].address)
# get instruction bytes of gadget
print bytes(gadgets[0].bytes).encode('hex')
# search gadgets
found = search(gadgets, 'mov e?x')
# remove all gadgets containing bad bytes in address
withouthBadBytes = filterBadBytes(gadgets, '000a0d')
# delete duplicates
withoutDuplicates = deleteDuplicates(gadgets)
strings = binary_elf.searchDataString('bin%')
for address, string in strings:
print "0x%x: %s" % (address, string)- Edit header fields;
- Print more informations;
For any other ideas please contact me