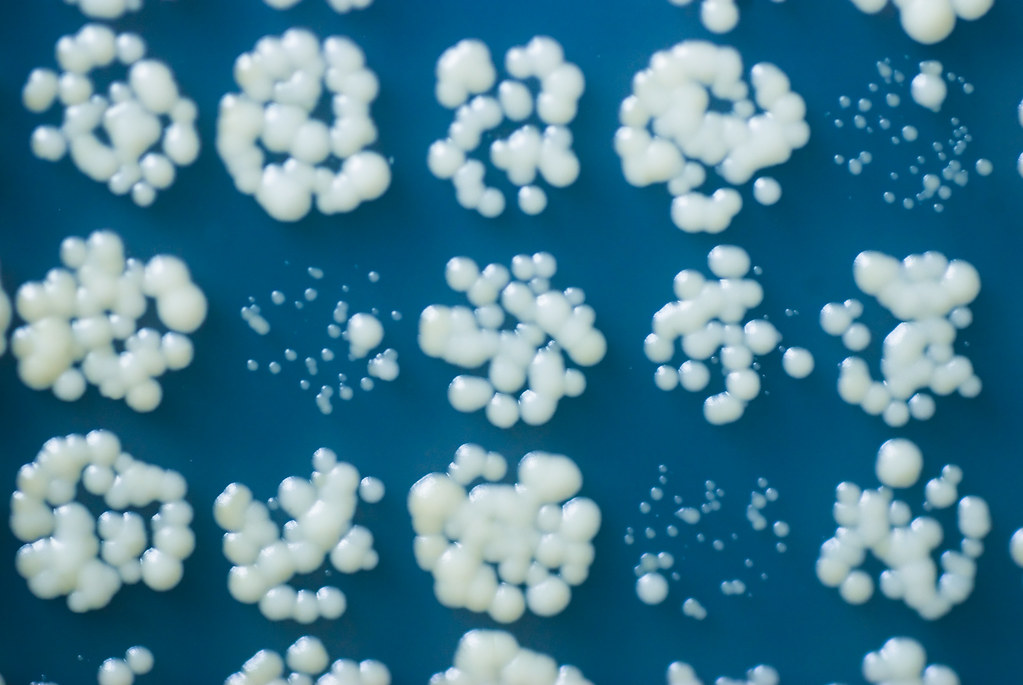
During Quantitative Fitness Analysis (QFA) of microbial cultures, we analyse the way cultures grow on solid agar surfaces. Basically, we inoculate cells onto an agar surface, and repeatedly photograph the agar plates as the populations grow, analysing images (using the Colonyzer software) to estimate changes in cell density over time. Usually we assume that cultures grow independently, and this is a good assumption during the early part of the growth phase. However, later in the growth phase, it seems likely that competition between cultures will become important. This model attempts to account for that competition.
CANS models are ODEs which we solve using the odeint function in Python.
On the way to developing a full-blown competition model, we developed some simpler versions, using the same tools:
See code in exponentialModel.py
t is time since inoculation
C is number of cells
C0 is the initial condition (number of cells at t=0)
r is the rate parameter
Assuming mass-action kinetics and assuming that the number of cells is continuous, we model the cell dynamics as a simple first order reaction in a well-stirred vessel:
C -> 2C
rate = r*C
The reaction above can be written in ODE form:
dC/dt = r * C
C(0) = C0
Which does have an anlytical solution:
C(t)=C0*exp(r*t)
However, for consistency with more complicated models to come, we solve this using the odeint function in Python.
Cells need nutrients to divide and the reaction C -> 2C is proportional to the availability of N
C + N -> 2C
rate = r*N*C
The rate of change of N and C can be written in the ODE form:
dC/dt = r * N * C
dN/dt = -(r * N * C)
C(0) = C0
N(0) = N0
The competition model takes into account the fact that nutrients can diffuse accross agar, therefore spots with large neighbours will be at a disadvantage when compared to spots with small neighbours.
In the data folder is an example of plate 15 from Addinall et al. 2011. This plate has several replicate cultures of a range of genotypes relevant to telomere biology. The image timecourse has been analysed by executing:
colonyzer -cp
Output_Images contains analysed previews demonstrating success of automatic colony location and image segmentation. Output_Data contains tab-delimited text files filled with quantitative cell density estimates generated by Colonyzer. Output_Reports contains plots in a multiple-page .pdf document, demonstrating how spot location and thresholding algorithms worked.
- Finish description of models in .md file
- Fit models to data (parameter inference)
- Compare inferred paramter values from competition model with values from regular QFA
- Universally Sloppy Parameter Sensitivities in Systems Biology Models http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.0030189
- Agar diffusion model http://web.mit.edu/rsi/2014/all/yjreo.pdf.gz