#FIWARE Lab monitoring system (based on Ceilometer and Monasca)
The following figure describes the high level architecture of the monitoring system.
Data is collected through Ceilometer (where customized pollsters have been developed) from each node. Relevant metrics are sent to Monasca on master node using Monasca-Ceilometer plugin. Additionally, the external Sanity Check tool from FIHealth publishes the sanity status of the nodes directly to Monasca.
Monitoring data is stored at Monasca master node and eventually passed to the FIWARE Big Data GE (Cosmos) for aggregation and analysis. FIWARE Lab Monitoring API component makes such data available to different clients, particularly to Infographics. This way Infrastructure Owners (IOs) should be able to track the following resources of their Openstack environments:
- region
- hosts
- images
- host services (OpenStack services: nova, glance, cinder, ... )
- instances (i.e. VMs)
Some additional information about Ceilometer: it is a tool created in order to handle the Telemetry requirements of an OpenStack environment (this includes use cases such as metering, monitoring, and alarming to name a few).
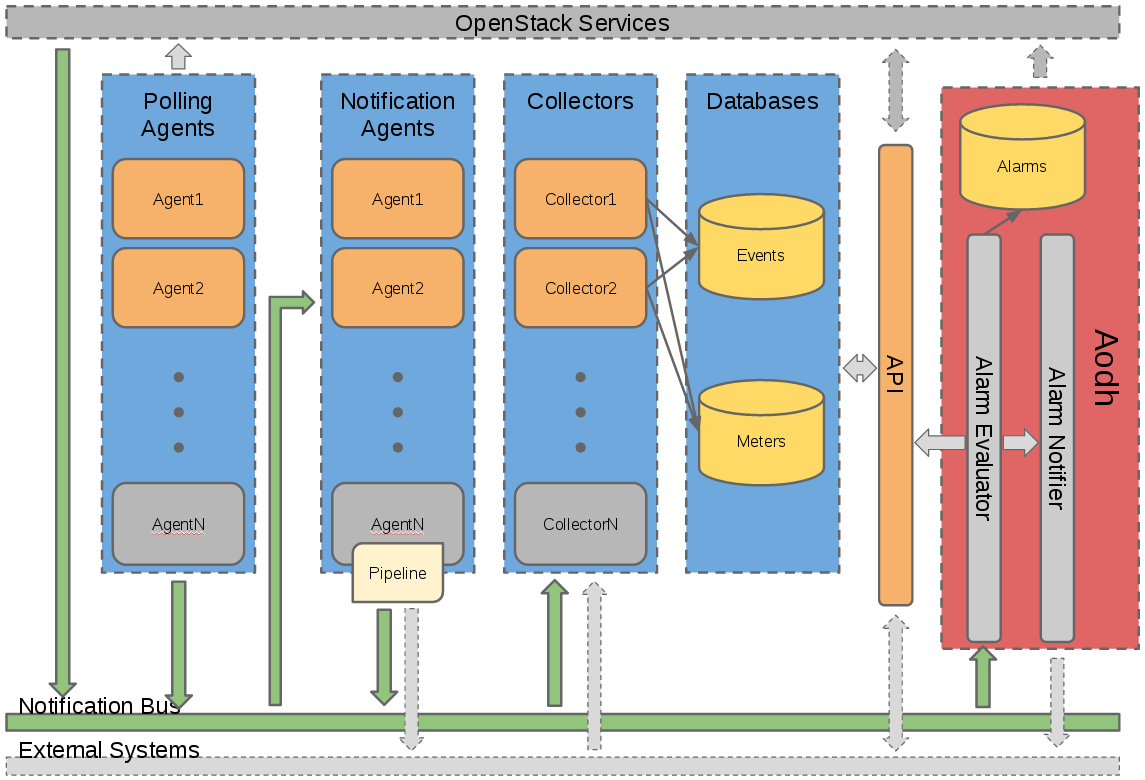
The installation and configuration procedure involves both Central agent pollsters at the controller nodes and Compute agent pollsters at every compute node. This repository contains all the pollsters and files that IOs would need to customize the default Ceilometer installation.
For the pollster installation, specific Ansible recipes are available together with related instructions in this guide.
Please follow these steps:
-
Open the file
/etc/ceilometer/ceilometer.confand add these entries (with your region values) at the end:[region] latitude=1.1 longitude=12.2 location=IT netlist=net04_ext,net05_ext ram_allocation_ratio=1.5 cpu_allocation_ratio=16Pay attention to the
netlistattribute: the names of external networks in your OpenStack installation. -
Locate the installation directory of Ceilometer package (usually,
pipcommand shows such information):# pip show ceilometer --- Name: ceilometer Version: 2015.1.1 Location: /usr/lib/python2.7/dist-packagesIn this documentation we will refer to such location as
$PYTHON_SITE_PKG. -
Copy region directory structure from this repository into Ceilometer package location (by default, at
$PYTHON_SITE_PKG/ceilometer). After that,RegionPollsterclass should be available:# python -c 'from ceilometer.region import region; print region.RegionPollster().__class__' <class 'ceilometer.region.region.RegionPollster'> -
Locate the entry points file for Ceilometer (which depends on the version: for 2015.1.1, should be located at path
$PYTHON_SITE_PKG/ceilometer-2015.1.1.egg-info/entry_points.txt) and please add the new pollster at the[ceilometer.poll.central]section:region = ceilometer.region.region:RegionPollster -
Restart Ceilometer Central Agent:
If using Fuel HA:
# crm resource restart p_ceilometer-agent-centralOtherwise:
# service ceilometer-agent-central restart
-
Add these entries to the file
/etc/nova/nova.confat section[DEFAULT]and restart the nova-compute service:compute_monitors = ComputeDriverCPUMonitor # The below line is suggested for > Kilo but the above will work, too: # - https://greencircle.vmturbo.com/docs/DOC-4125-enabling-cpu-metrics-in-openstack # - https://docs.openstack.org/newton/config-reference/compute/config-options.html # - https://docs.openstack.org/mitaka/config-reference/compute/config-options.html # compute_monitors = nova.compute.monitors.cpu.virt_driver notification_driver = messagingv2 -
Copy host.py file from the compute_pollster directory of this repository into the
compute/pollsters/subdirectory at Ceilometer package location. After that,HostPollsterclass should be available:# python -c 'from ceilometer.compute.pollsters import host; print host.HostPollster().__class__' <class 'ceilometer.compute.pollsters.host.HostPollster'> -
Edit entry points file to add the new pollster at the
[ceilometer.poll.compute]section:compute.info = ceilometer.compute.pollsters.host:HostPollster -
Please check the polling frequency defined by
intervalparameter at/etc/ceilometer/pipeline.yaml. Its default value is 60 seconds: you may consider lowering the polling rate. -
Restart both Nova Compute and Ceilometer Compute Agent:
# service nova-compute restart # service ceilometer-agent-compute restart
-
Copy (or merge) the following configuration files from config/compute directory into
/etc/ceilometer:pipeline.yaml -
Restart Compute Agent.
# service ceilometer-agent-compute restart
Please follow these steps to install in all controller nodes the Python plugin and storage driver for Ceilometer to send samples to Monasca:
-
Install python-monascaclient:
# pip install python-monascaclient==1.0.27 -
Copy the following files from Ceilosca component (included in the latest release of Monasca-Ceilometer) into the Ceilometer package location
$PYTHON_SITE_PKG/ceilometer:monasca_client.py storage/impl_monasca.py storage/impl_monasca_filtered.py publisher/monasca_data_filter.py publisher/monasca_metric_filter.py publisher/monclient.py -
Edit the entry points file to add the following entries:
At
[ceilometer.publisher]section:monasca = ceilometer.publisher.monclient:MonascaPublisherAt
[ceilometer.metering.storage]section:monasca = ceilometer.storage.impl_monasca_filtered:Connection -
Copy (or merge) the following configuration files from config/controller directory into
/etc/ceilometer:pipeline.yaml monasca_field_definitions.yamlPlease ensure elements in meter_source include the subset of Ceilometer metrics required by FIWARE Monitoring (this should be the case without any modifications) and don't forget to set Monasca endpoint at Master Node in the publishers of meter_sink:
sinks: - name: meter_sink transformers: publishers: - notifier:// - monasca://http://MONASCA_IP:8070/v2.0 -
Modify
/etc/ceilometer/ceilometer.confto configure a new meter storage driver for Ceilometer (substitute with the endpoint of Master Node):metering_connection = monasca://http://MONASCA_IP:8070/v2.0Please make sure the user specified under
[service_credentials]section of the same file has monasca_user role added. -
Restart all Ceilometer services:
If using Fuel HA:
# crm resource restart p_ceilometer-agent-central # crm resource restart p_ceilometer-alarm-evaluator # service ceilometer-agent-notification restart # service ceilometer-collector restart # service ceilometer-api restart # service ceilometer-alarm-notifier restartOtherwise:
# CEILOMETER_SERVICES=$(cd /etc/init.d; ls -1 ceilometer*) # for NAME in $CEILOMETER_SERVICES; do service $NAME restart; done
In order to monitor the OpenStack services (i.e. host services), monasca-agent should be installed in all the controllers:
-
Create a Python virtualenv located at
/opt/monasca:# cd /opt # virtualenv monasca # source monasca/bin/activate -
Please install
pbrafter upgrading your versions ofsetuptoolsandpip:(monasca)# pip install --upgrade setuptools (monasca)# pip install --upgrade pip (monasca)# pip install pbr==1.10.0 (monasca)# pip install positional==1.1.0 -
Locate the latest release of Monasca Agent component and use
piptool to install it. For instance, to install version "1.1.21-FIWARE", please run:(monasca)# VERSION=1.1.21-FIWARE (monasca)# PBR_VERSION=$VERSION pip install git+https://github.com/telefonicaid/monasca-agent.git@$VERSION -
Configure the component using
monasca-setup(as described in the documentation). Note that you will have to provide:- Your region name
- The address or domain name of Monasca API
- Valid Keystone credentials, usually those of the Ceilometer service (which should have previously been assigned the monasca_user role)
- The frequency period in seconds (default is 10 minutes)
(monasca)# monasca-setup \ --username=YOUR_CEILOMETER_USER \ --password=THE_PASSWORD \ --project_name=service \ --keystone_url=http://cloud.lab.fiware.org:4731/v3 \ --monasca_url=http://MONASCA_IP:8070/v2.0 \ --dimensions=region:YOUR_REGION --check_frequency=600 -
Only the file
process.yamlused by Process Checks plugin is required at/etc/monasca/agent/conf.d/. Please ensure it is configured to monitor all OpenStack services (this should be the case without any modifications, but it is appropriate to check that all of your services are monitored). The example below shows configuration information for one service (nova-scheduler):- built_by: Nova detailed: false dimensions: component: nova-scheduler service: compute exact_match: false name: nova-scheduler search_string: - nova-scheduler -
Please verify the configuration is correct:
# service monasca-agent configtest -
Finally, restart the agent:
# service monasca-agent restart
In order to verify whether the installation and configuration of FIWARE Monitoring have been successful, we provide the fiware-check-monitoring.sh script available at tools folder. It performs a set of checks, not only in the controller itself but also in the compute nodes, and shows results in a human-readable manner.
Running the script at the controllers with no additional parameters may suffice in most of the cases, although command
line options allow further adjustments. Script only requires defining the standard OpenStack environment variables with
the credentials needed to run nova and other commands.
For full information about the usage and options, please type: fiware-check-monitoring.sh --help
The former script will give us very comprehensive information about the installation and will also retrieve real metrics and measurements to ensure FIWARE Monitoring is working properly. In any case, we could optionally try some queries using the command line client of Ceilometer, like these:
-
Monitoring information about the region (please replace RegionOne with yours):
# ceilometer resource-list -q resource_id=RegionOne +-------------+-----------+---------+------------+ | Resource ID | Source | User ID | Project ID | +-------------+-----------+---------+------------+ | RegionOne | openstack | None | None | +-------------+-----------+---------+------------+ -
Monitoring information about one of your compute nodes (please note that the metric resource_id is the concatenation <host>_<nodename>, values which are usually the same):
# HOST_RESOURCE_ID=$(nova host-list | awk '/compute/ {print $2 "_" $2; exit}') # ceilometer meter-list -q resource_id=$HOST_RESOURCE_ID +--------------------------+-------+------+---------------------------+---------+------------+ | Name | Type | Unit | Resource ID | User ID | Project ID | +--------------------------+-------+------+---------------------------+---------+------------+ | compute.node.cpu.percent | gauge | % | node-2.aa.bb_node-2.aa.bb | None | None | | compute.node.cpu.max | gauge | cpu | node-2.aa.bb_node-2.aa.bb | None | None | | compute.node.cpu.now | gauge | cpu | node-2.aa.bb_node-2.aa.bb | None | None | | compute.node.cpu.tot | gauge | cpu | node-2.aa.bb_node-2.aa.bb | None | None | | compute.node.disk.max | gauge | GB | node-2.aa.bb_node-2.aa.bb | None | None | | compute.node.disk.now | gauge | GB | node-2.aa.bb_node-2.aa.bb | None | None | | compute.node.disk.tot | gauge | GB | node-2.aa.bb_node-2.aa.bb | None | None | | compute.node.ram.max | gauge | MB | node-2.aa.bb_node-2.aa.bb | None | None | | compute.node.ram.now | gauge | MB | node-2.aa.bb_node-2.aa.bb | None | None | | compute.node.ram.tot | gauge | MB | node-2.aa.bb_node-2.aa.bb | None | None | +--------------------------+-------+------+---------------------------+---------+------------+ -
Monitoring information about one of your images:
# IMAGE_NAME="base_centos_6" # IMAGE_RESOURCE_ID=$(nova image-show $IMAGE_NAME | awk '$2=="id" {print $4}') # ceilometer meter-list -q resource_id=$IMAGE_RESOURCE_ID +-------+-------+-------+--------------------------------------+---------+----------------------------------+ | Name | Type | Unit | Resource ID | User ID | Project ID | +-------+-------+-------+--------------------------------------+---------+----------------------------------+ | image | gauge | image | 66d7c0ee-3929-4dbf-ac8e-39e17f44c445 | None | 00000000000003228460960090160000 | +-------+-------+-------+--------------------------------------+---------+----------------------------------+ -
Monitoring information about one of the active instances:
# INSTANCE_ID=$(nova list --all-tenants | awk '/ACTIVE/ {print $2; exit}') # ceilometer meter-list -q resource_id=$INSTANCE_ID +-----------------+-------+----------+--------------------------------------+----------+----------------------------------+ | Name | Type | Unit | Resource ID | User ID | Project ID | +-----------------+-------+----------+--------------------------------------+----------+----------------------------------+ | instance | gauge | instance | 389190e8-6b55-4260-8b74-ee3a073e729d | somebody | 00000000000000000000000000004980 | | cpu_util | gauge | % | 389190e8-6b55-4260-8b74-ee3a073e729d | somebody | 00000000000000000000000000004980 | | disk.capacity | gauge | B | 389190e8-6b55-4260-8b74-ee3a073e729d | somebody | 00000000000000000000000000004980 | | disk.usage | gauge | B | 389190e8-6b55-4260-8b74-ee3a073e729d | somebody | 00000000000000000000000000004980 | | memory | gauge | MB | 389190e8-6b55-4260-8b74-ee3a073e729d | somebody | 00000000000000000000000000004980 | | memory.usage | gauge | MB | 389190e8-6b55-4260-8b74-ee3a073e729d | somebody | 00000000000000000000000000004980 | +-----------------+-------+----------+--------------------------------------+----------+----------------------------------+To query for the exact measurement values:
# ceilometer sample-list -q resource_id=$INSTANCE_ID -m memory.usage --limit 3 +--------------------------------------+--------------+-------+--------+------+---------------------------+ | Resource ID | Name | Type | Volume | Unit | Timestamp | +--------------------------------------+--------------+-------+--------+------+---------------------------+ | 389190e8-6b55-4260-8b74-ee3a073e729d | memory.usage | gauge | 140.0 | MB | 2016-06-16T11:25:44+00:00 | | 389190e8-6b55-4260-8b74-ee3a073e729d | memory.usage | gauge | 140.0 | MB | 2016-06-16T11:26:44+00:00 | | 389190e8-6b55-4260-8b74-ee3a073e729d | memory.usage | gauge | 140.0 | MB | 2016-06-16T11:27:44+00:00 | +--------------------------------------+--------------+-------+--------+------+---------------------------+
Apache License, Version 2.0, January 2004
