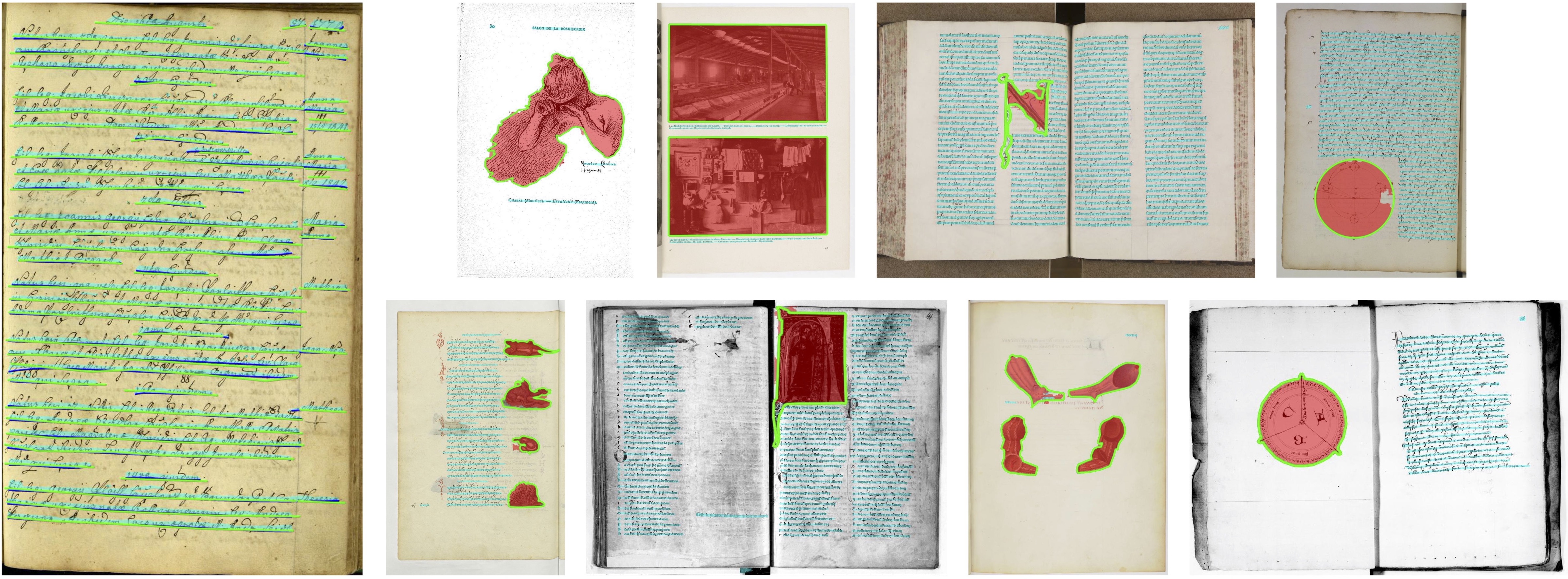
Pytorch implementation of "docExtractor: An off-the-shelf historical document element extraction" paper:
Make sure you have Anaconda installed (version >= to 4.7.10, you may not be able to install correct dependencies if older). If not, follow the installation instructions provided at https://docs.anaconda.com/anaconda/install/.
conda env create -f environment.yml
conda activate docExtractor
The following command will download:
- synthetic resources needed to generate SynDoc (manually collected ones and Wikiart dataset)
- our trained model
- IlluHisDoc dataset
./download.sh
There are several main usages you may be interested in:
- perform element extraction (off-the-shelf using our trained network or a fine-tuned one)
- build our segmentation method from scratch
- fine-tune network on custom datasets
In the demo folder, we also provide a jupyter notebook and its html version detailing a
step-by-step pipeline to predict segmentation maps for a given image.
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=gpu_id python src/extractor.py --input_dir inp --output_dir out
Main args
-i, --input_dir: directory where images to process are stored (e.g.raw_data/test)-o, --output_dir: directory where extracted elements will be saved (e.g.results/output)-t, --tag: model tag to use for extraction (default is our trained network)-l, --labels: labels to extract (default corresponds to illustration and text labels)-s, --save_annot: whether to save full resolution annotations while extracting
Additionals
-sb, --straight_bbox: whether to use straight bounding boxes instead of rotated ones to fit connected components-dm, --draw_margin: Draw the margins added during extraction (for visual or debugging purposes)
NB: check src/utils/constant.py for labels mapping
NB: the code will automatically run on CPU if no GPU are provided/found
This would result in a model similar to the one located in models/default/model.pkl.
python src/syndoc_generator.py -d dataset_name -n nb_train --merged_labels
-d, --dataset_name: name of the resulting synthetic dataset-n, --nb_train: nb of training samples to generate (0.1 x nb_train samples are generated for val and test splits)-m, --merged_labels: whether to merge all graphical and textual labels into uniqueillustrationandtextlabels
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=gpu_id python src/trainer.py --tag tag --config syndoc.yml
To fine-tune on a custom dataset, you have to:
- annotate a dataset pixel-wise: we recommend using VGG Image Anotator
(link) and our
ViaJson2Imagetool - split dataset in
train,val,testand move it todatasetsfolder - create a
configs/example.ymlconfig with corresponding dataset name and a pretrained model name (e.g.default) - train segmentation network with
python src/trainer.py --tag tag --config example.yml
Then you can perform extraction with the fine-tuned network by specifying the model tag.
NB: val and test splits can be empty, you just won't have evaluation metrics
python src/via_converter.py --input_dir inp --output_dir out --file via_region_data.json
NB: by default, it converts regions using the illustration label
python src/synline_generator.py -d dataset_name -n nb_doc
NB: you may want to remove text translation augmentations by modifying
synthetic.element.TEXT_FONT_TYPE_RATIO.
python src/iiif_downloader.py -f filename.txt -o output_dir --width W --height H
-f, --file: file where each line contains an url to a json manifest-o, --output_dir: directory where downloaded images will be saved--widthand--height: image width and height respectively (default is full resolution)
NB: Be aware that if both width and height arguments are specified, aspect ratio
won't be kept. Common usage is to specify a fixed height only.
If you find this work useful in your research, please consider citing:
@inproceedings{monnier2020docExtractor,
title={{docExtractor: An off-the-shelf historical document element extraction}},
author={Monnier, Tom and Aubry, Mathieu},
booktitle={ICFHR},
year={2020},
}