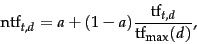Document analysis and natural language processing using the New York Times API Newswire API.
The goal is to cluster the abstracts of some articles from the New York Times newspaper.
Information on tf-idf was found at the Introduction to Information Retrieval book online. In particular, see the inverse document frequency and tf-idf weighting sections.
From wikipedia: tf–idf, short for term frequency–inverse document frequency, is a numerical statistic that is intended to reflect how important a word is to a document in a collection or corpus.
We are using raw frequencies for this project. Namely, the raw number of times that a term t appears in the document d.
This presents an issue when using longer documents. To normalize the term frequencies we can use the normalized term frequency equation:
Notice that this is called "augmented" frequency in the wikipedia article for tf-idf.
Where a is a smoothing coefficient between 0 and 1. The NLP book at stanford recommends setting this to 0.4
An alternative approach is boolean frequencies where:
tf(t,d) = 1 if t occurs in d and 0 otherwise
The inverse document frequency is a measure of how much information the word provides, that is, whether the term is common or rare across all documents. It is the logarithmically scaled fraction of the documents that contain the word, obtained by dividing the total number of documents by the number of documents containing the term, and then taking the logarithm of that quotient.
tfidf(t,d,D) = tf(t,d) * idf(t,D)
The Python NLTK package was primarily used for the NLP tasks of this project.
Part 1 of this homework consists on downloading data using an API. The NY Times API is available at http://developer.nytimes.com. It provides access to various articles, both historic and new. For this assignment we are interested in the Times NewswireAPI, which provides access to articles, blogs, and so on, as they are being produced. For each article we can obtain directly from the API its URL and its abstract, among other information. Your tasks for this section of the problem are the following:
(1) Downloading the data (5 pts)
-
Study the API, download 50,000 different articles from the Times Newswire API.
-
For each of them save the URL and the abstract. Note that because articles are created continually, you may end up downloading some articles multiple times; you should make sure that you do not store each article more than once.
-
For each article assign a unique docID. Note that this part is not completely trivial because often the API does not return the expected document, so you need to catch the exceptions thrown, put the right delays, and retry, for some steps.
Review: The map function takes four parameters which by default correspond to:
a. WritableComparable key - the byte-offset of the current line in the file
b. Writable value - the line from the file
c. OutputCollector - output - this has the .collect method to output a <key, value> pair
d. Reporter reporter - allows us to retrieve some information about the job (like the current filename)
(2) Preprocessing of the abstracts. (10 pts)
-
Your map function should extract individual words from the input it is given, and output the word as the key, and the current filename as the value. Thus, the map function (or one of them) should output <"word", "filename"> pairs.
-
Remove all punctuation and numbers, and keep only the words.
-
Convert each word to lowercase, remove stopwords.
-
Extra credit (+2 pts): perform word stemming (see for example Porter’s stemmer or the NLTK python package)
Hints:
-
Since in this example we want to output <"word", "filename"> pairs, the types will both be Text.
-
The word count program had an example of extracting individual words from a line
-
To get the current filename, use the following code snippet:
FileSplit fileSplit = (FileSplit)reporter.getInputSplit(); String fileName = fileSplit.getPath().getName();
(3) TF-IDF (5 pts)
-
For each document compute its tf-idf vector as explained in *******
-
Extra credit (+2 pts): Normalize with respect to document length
- Note that to accomplish this section of the homework you might need to perform a series of MR jobs and not just a single job
Perform clustering using as features the vector space produced by tf-idf
(4) Use a clustering algorithm of your choice (10 pts)
-
Explain why did you chose that particular algorithm, what are pros and cons
-
Explain design decisions with respect to the number of clusters (if applicable)
-
Extra credit (+2 pts): use a quantitative approach to select the ‘best’ number of clusters (if applicable)
(5) Perform a statistical analysis about the top 20 most discriminative terms per cluster (5 pts)
- Use tf-idf scores to find most discriminative terms per cluster
(6) Present a visualization of clusters and term frequencies (5 pts)
-
Use any graphic/visualization program of your choice
-
Be creative and present useful graphs
(7) Submit a presentation explaining/describing/showing clearly each of the previous 6 points. After submission, no further changes to your presentation will be allowed
Total: 40 points + 6 extra credit proportional to 23 points of your final grade
For each bullet and number, there should be a point on the presentation that addresses this aspect, as this is how the presentation will be graded.