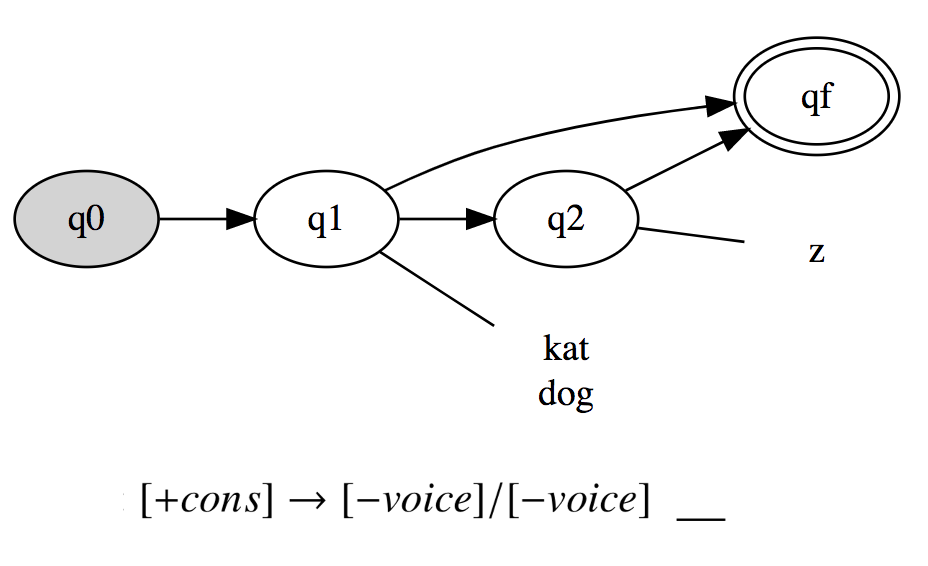
Full paper: http://ling.auf.net/lingbuzz/003665
- Build the project image
$ sudo docker build . -t taucompling/morphophonology_spe:latest -f ./docker/Dockerfile
** Note: if build fails with a gcc error, try increasing the memory and/or swap size in Docker settings. **
- Start the Docker container
$ docker run -i -t -v ~/logs/:/root/morphophonology_spe/logs/ taucompling/morphophonology_spe:latest
Parameters explained:
-i- Interactive shell-t- Spawn a terminal-v- Mount logs directory for persistence
- Activate the Python virtual environment
$ source ~/venv/bin/activate
You will need Python 3.6.
$ virtualenv -p $(which python3.6) venv
$ source ./venv/bin/activate
- Download OpenFst 1.6.0 from
http://www.openfst.org/twiki/pub/FST/FstDownload/openfst-1.6.0.tar.gz - Unzip, untar:
$ tar xzvf openfst-1.6.0.tar.gz $ ./configure && make install- Run:
$ export CFLAGS="-std=c++11 -stdlib=libc++ -mmacosx-version-min=10.7" - You may need to add
-L/usr/local/libtoCFLAGS - Run:
$ export CPATH="/usr/local/include"-std=c++11makes the compiler use the correct C standard for OpenFst-stdlib=libc++makes the compiler use the standard C library OpenFst uses
$ pip install pyfst$ unset CFLAGS
A Python library for multiple-precision arithmetic.
MacOS:
$ brew install gmp
$ pip install gmpy
Ubuntu/Debian:
$ sudo apt-get install libgmp3-dev
$ pip install gmpy
$ pip install -r requirements.txt
$ python run_genetic_algorithm.py
Options:
-i SIMULATION_ID, --id
Simulation ID
-s SIMULATION_NAME, --simulation
Simulation name, e.g "french_deletion"
-e ENVIRONMENT_NAME, --environment
Environment to use for migration and logging: "aws", "azure", or "local". Default: "local"
-n TOTAL_ISLANDS, --total-islands
Total number of islands in entire simulation
(including remote machines)
-r, --resume Resume simulation from dumped islands
--first-island
First island index on this machine. Default: 0
--last-island
Last island index on this machine. Default: number of islands minus 1
$ python run_genetic_algorithm.py -i french_deletion_test -s french_deletion -n 200
-
Machine #1 with 200 islands:
$ python run_genetic_algorithm.py -i french_deletion_test -s french_deletion -n 400 --first-island 0 --last-island 199 -
Machine #2 with another 200 islands:
$ python run_genetic_algorithm.py -i french_deletion_test -s french_deletion -n 400 --first-island 200 --last-island 399
Saved to ./logs/genetic_log.txt
- In file
_fst.pyx.tpl, change line 814 to:
out_str = out.str().decode('utf8')
- Compile:
cd fst
cat types.yml | mustache - _fst.pyx.tpl > _fst.pyx
cat types.yml | mustache - libfst.pxd.tpl > libfst.pxd
cython --cplus _fst.pyx- Install:
python setup.py install $ python run_ilm_simulation.py
usage: run_ilm_simulation.py -i SIMULATION_ID -s SIMULATION_NAME
[-e ENVIRONMENT_NAME] -n TOTAL_ISLANDS
[-r RESUME_SIMULATION] -g GENERATIONS
[--ilm-bottleneck ILM_BOTTLENECK]
[--noise-rate NOISE_RATE] [-t TOTAL] [-m MACHINE]
required arguments:
-i SIMULATION_ID, --id SIMULATION_ID
Simulation ID
-s SIMULATION_NAME, --simulation SIMULATION_NAME
Simulation name, e.g "dag_zook_devoicing"
-n TOTAL_ISLANDS, --total-islands TOTAL_ISLANDS
Total number of islands in entire simulation
(including other machines)"
-g GENERATIONS, --generations GENERATIONS
Number of ILM generations to run.
optional arguments:
-e ENVIRONMENT_NAME, --environment ENVIRONMENT_NAME
Environment to use for migrations: "aws", "azure", or
"local". Default: "local"
-r RESUME_SIMULATION, --resume RESUME_SIMULATION
Resume simulation from given generation
--ilm-bottleneck ILM_BOTTLENECK
% of words to pass to the next generation. Integer.
Default is 100.
--noise-rate NOISE_RATE
% of words to apply noise to in the data passed to the
next generation. Default is 0.
ILM machines:
-t TOTAL, --total-machines TOTAL
total machines this simulation is running on
-m MACHINE, --machine MACHINE
Machine number between 1 and TOTAL (inclusive)
$ python run_ilm_simulation.py -i ilm-tak-soo -s tag_soo_ilm_final_devoicing -n 100 -g 350 --ilm-bottleneck 80 --noise-rate 2
- Machine #1 with 200 islands:
$ python run_ilm_simulation.py -i ilm-tak-soo -s tag_soo_ilm_final_devoicing -n 400 -g 350 --ilm-bottleneck 80 --total-machines 2 --machine 1 - Machine #2 with another 200 islands:
$ python run_ilm_simulation.py -i ilm-tak-soo -s tag_soo_ilm_final_devoicing -n 400 -g 350 --ilm-bottleneck 80 --total-machines 2 --machine 2
The script calculates the number of islands to run on each machine according to
the values of -n, -m, -t arguments