Hyperion is an engine designed to launch and monitor user defined components using YAML configuration files.
Inspired by vdemo and TMuLE (see vdemo and TMuLE assessment)
Hyperion (like TMuLE) is written in Python and utilizes the tmux library for python to start components in detached sessions. For each host defined in the components a master session is created, in which each component will be started in a window. Components are managed by a main server that delegates commands to slave server instances on remote machines and forwards information to subscribed user interfaces.
This package strictly separates optional content from the core which reflects in the install options.
The minimal Hyperion package can be installed via setuptools python setup.py install or via pip pip install .
To enable dependency graph visualisation, you need to install via pip with pip install -e .[GRAPH] (if you are running zsh, you need to escape the brackets: pip install -e .\[GRAPH\]).
If you want to use the interactive cli based on urwid, install with pip install -e .[I-CLI].
If you wish to use the PyQt gui, Qt4 for python has to be installed via a package manager (apt install python-qt4 on debian based distributions). This is due to the fact, that the PyQt4 package can not be managed by pip. Hyperion is able to detect if PyQt4 is installed at runtime and if so enable the GUI features.
To make use of all optional features, run the install with pip install -e .[FULL]. Note that to use the PyQt gui you still need to install the python-qt4 package manually.
Hyperion supports various modes:
usage: hyperion server --config CONFIG [-h] [-p PORT]
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-p PORT, --port PORT Define the TCP port on which the backend will listen
for clients. Default: 23081
Server mode starts a component manager as master that listens for clients on the specified port (if none is given defaults to 23081) and connects to remote machines starting slave instances. Clients can connect to the server to issue commands or request information from the manager.
usage: hyperion --config CONFIG execute [-h] { -l | ([-C COMP [COMP ...]] ( -s | -k | -c | -L | -T))}
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-C COMP [COMP ...], --component COMP [COMP ...]
single component or list of a components
-l, --list List all available components
-s, --start start the component
-k, --stop Stop the component
-c, --check Check the component
-L, --log Show the component log
-T, --term Show the component term
The execute mode will initialize the configured system with the executing host as controlling instance. It offers to run a specific action for a single component or a list of components and exit.
usage: hyperion ui [-h] [-p PORT] [-H HOST | --no-socket] [-x]
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-p PORT, --port PORT Specify port to connect to. Defaults to 23081
-H HOST, --host HOST Specify host to connect to. Defaults to localhost
--no-socket Start in standalone mode without connecting to a
running backend
-x Use PyQt gui (requires X server and python-qt4
package)
UI mode starts a user interface (PyQt or interactive cli) which either connects to a running hyperion backend or if started in standalone mode runs its own backend. Note that the backend created by standalone mode will terminate when the ui is exited and unlike a backend started by server mode, it will not accept connections from other uis.
Visit Control GUI for detailed information about the GUI.
Visit Interactive CLI for detailed information about the interactive cli.
hyperion --config systems/demo.yaml validate [-h] [--visual]
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--visual Generate and show a graph image
The validation mode parses the dependencies specified in the component configuration files and checks whether they are all met makes sure the directed dependency graph is acyclic (no circular dependencies) to check if starting all components with their dependencies is possible. Errors (unmet and circular dependencies) are displayed on the cli. If the configuration is valid, a list showing the order for a full system start is printed on the cli.
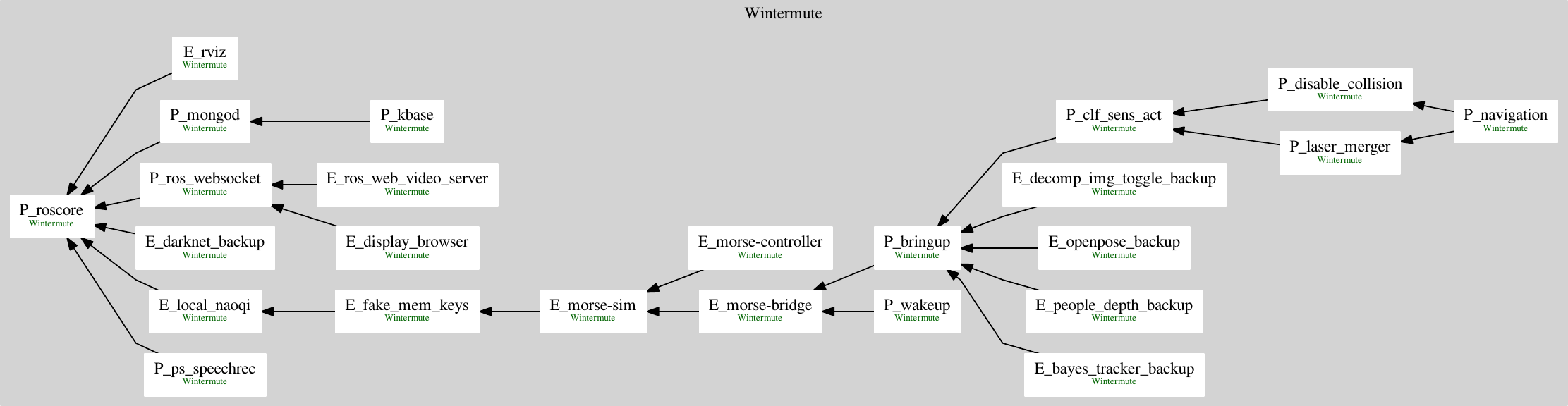
By specifying the visual argument, the command will generate an image of the the dependency graph (highlighting errors). Please note: if a circular dependency error is detected, the graph will be incomplete because the algorithm won't be able to iterate through the remaining nodes!
Image: Graph generated with the sample components with missing dependency error (December 2018)
Image: Graph generated from intermediate scale robotic simulation system (December 2018)
hyperion --config systems/demo.yaml edit
The editor mode is planned to provide an editor GUI to create and edit components, groups and systems. The main idea is, to prevent misconfiguration by syntax errors in the configuration files and to help configure dependencies. This feature will use the validation mode.
hyperion slave --config CONFIG [-h] -p PORT -H HOST
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-p PORT, --port PORT specify port of the master server to connect to
-H HOST, --host HOST specify master server hostname to connect to
The slave mode launches a limited version of a manager server which immediately connects to a master server on the given host at the given port. It features starting, stopping and checking local components and will forward monitoring events and check results to the master server. Note that the slave mode is not intended to by started by hand, but by a master server.
tmux >= 1.8 is required to handle libtmux's calls.
system config names are not allowed to contain a space!
For more information about the developement and upcoming features visit the wiki