This is a work in progress DIY split-flap display. Prototype two-character display: video.
The goal is to make a low-cost display that's easy to fabricate at home in small/single quantities (e.g. custom materials can be ordered from Ponoko or similar, and other hardware is generally available).
The 3d model is built using OpenSCAD in 3d/splitflap.scad, the driver board is designed in KiCad in electronics/splitflap.pro, and the driver firmware is written using Arduino in arduino/splitflap/splitflap.ino.
This design is currently at a prototype stage. The source files provided here were able to produce a working prototype (with some manual modifications to correct for slight errors/omissions), but aren't necessarily recommended yet unless you enjoy incomplete documentation, frustration, and adventure!
NOTE: There is active work ongoing to redesign the electronics to make it easier for a beginner hobbyist to build, so keep an eye out for changes, or track progress on issue #12.
| Component | Status | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Enclosure/Mechanics | Release Candidate | Need documentation on ordering. |
| Electronics | Beta | Works but requires SMD soldering experience. A new electronics/driver design is in progress - see #12 |
| Firmware | Alpha | Works, but is being revamped as part of the new electronics design from #12 |
| Control Software | none | No work started; currently manual control using Arduino Serial Monitor |
I'd love to hear your thoughts and questions about this project, and happy to incorporate any feedback you might have into these designs! Please feel free (and encouraged) to open GitHub issues, email me directly, reach out on Twitter, and get involved in the open source development and let's keep chatting and building together!
- laser cut enclosure and mechanisms from a single material
- cheap, widely available 28byj-48 stepper motor (less expensive than NEMA-17 motors, and doesn't require an expensive high current stepper driver)
- CR80 PVC cards for flaps, cheap in bulk
- store-bought vinyl stickers for flap letters
This is an incomplete list of supplies needed to build a split-flap display module, to get a rough sense of the overall cost.
- $5/2 units -- MDF 3.2mm P2 on Ponoko
- $20 -- laser cutting on Ponoko (can save ~$0.70 by skipping engraved label)
- $7 -- shipping from Ponoko
- ~$2 -- 28byj-48 motor (12V preferred!) and ULN2003 driver (see motor notes for specific details)
- $6.39/2 units -- vinyl letter stickers (minimum letter duplication per pack is 2) on Amazon
- $12/5 units or $36/25 units -- CR80 cards (each CR80 card becomes 2 flaps, each unit requires 40 flaps) on Amazon or Amazon
- ~$10/10 units -- male-to-male 3-pin servo cable (for sensors) e.g. on Amazon
- ? -- M4x12mm button head bolts - ISO7380 e.g. on Amazon or AliExpress
- ? -- M4 nuts
TBD:
- $0.76 -- GP2S60 reflectance sensor on digikey
- $14/10 units -- PCB for reflectance sensor on seeedstudio
- $6.66/4 units -- ATmega32U4 microcontroller for driver board on digikey
- ? -- Other electronics components for driver/sensor boards
- ? -- 12V power supply
Tools (one-time, up front cost):
- $9.17 -- badge slot punch (for cutting notches out of cards to make flaps) on Amazon
This design is still a work in progress; a build log/instructions for building a prototype split-flap display of your own is posted in the wiki.
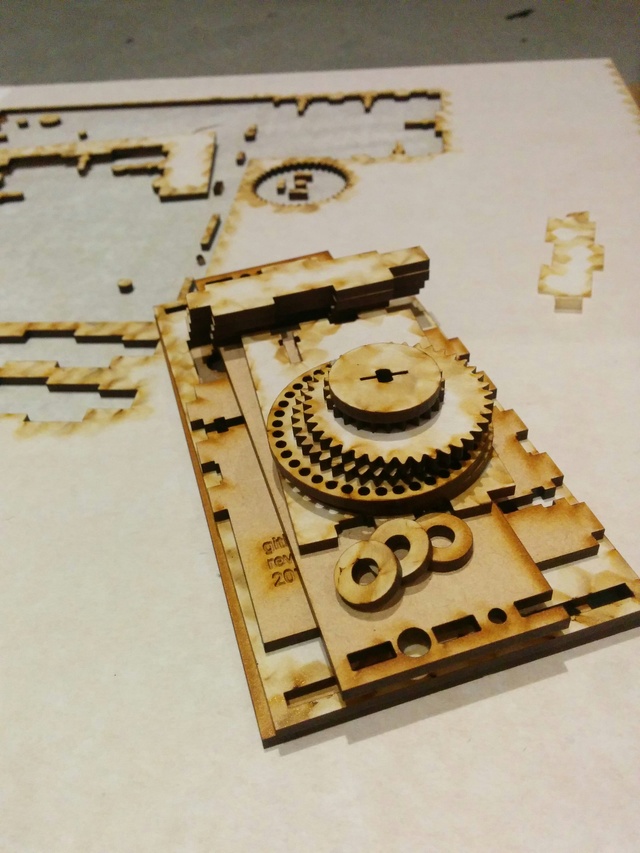

Important: most of the diagrams and downloadable files on this README page are auto-generated from the latest experimental code, which may be untested or broken. If you are interested in building one without digging into the design details much, I recommend using a stable design, as described in the wiki.
The main design file is 3d/splitflap.scad
You'll need a recent version of OpenSCAD (e.g. 2015-03), which may need to be installed through the PPA:
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:openscad/releases
In general, solid objects such as the gears or enclosure sides are built from 2d primitives and then extruded to the appropriate thickness for 3d rendering, rather than using 3d primitives. This simplifies the design without losing expressiveness; the perpendicular laser cut beam doesn't allow for cuts that vary in the Z dimension anyway.
Note that while the design is parameterized and many values may be tweaked, there is currently no error checking for invalid parameters or combinations of parameters. Please take care to validate the design if you change any parameters. For instance, while most of the design would correctly adjust to a tweaked material thickness value, the thickness plays a role in the alignment of the gears, so changing this value may result in misaligned gears or issues with the motor shaft length.
The design can be rendered to 2d for laser cutting by running 3d/generate_2d.py, which outputs to 3d/build/laser_parts/combined.svg
Internally, the design uses a projection_renderer module (3d/projection_renderer.scad), which takes a list of child elements to render, and depending on the render_index renders a single child at a time. It also adds material to each shape to account for the kerf that will be cut away by the laser.
The generate_2d.py script interacts with the projection_renderer module by first using it to determine the number of subcomponents to render, then runs OpenSCAD to export each component to an SVG file. It does some post-processing on the SVG output (notably adds "mm" to the document dimensions), and then combines all components into the single combined.svg output.
Once the combined.svg file is generated, you'll want to manually remove a couple redundant cut lines that are shared by multiple adjacent pieces, to save time/cost when cutting. In Inkscape, select the "Edit paths by nodes" tool and select an edge to delete - the endpoints should turn blue. Then click "Delete segment between two non-endpoint nodes", and repeat this for all other redundant cut lines.
Latest (Experimental!) Laser Cut Vector File: svg (In order to get the design laser-cut from Ponoko, you'll need to copy all of the shapes from that file into one of Ponoko's templates)
The design can be rendered to a rotating 3d animated gif (seen above) by running 3d/generate_gif.py, which outputs to 3d/build/animation/animation.gif
The generate_gif.py script runs multiple OpenSCAD instances in parallel to render the design from 360 degrees to individual png frames, which are then combined into the final gif animation. As part of building the animation, generate_gif.py renders the design with multiple configurations (opaque enclosure, see-through enclosure, no-enclosure and no flaps) by setting the render_enclosure and render_flaps variables.
The design can be rendered to a series of STL files (one per color used in the model) in order to be displayed in an interactive web-based 3d viewer. Similar to the projection_renderer used to render individual components for laser-cutting, the ColoredStlExporter detects all the colors used in the model and renders them one-by-one to separate STL files, along with a manifest that maps each STL file to its RGB color. The STL files and manifest are loaded using three.js to display an interactive model on a web site using WebGL. See this blog post for more details on how the export and three.js renderer work: OpenSCAD Rendering Tricks, Part 3: Web viewer.
There is a work-in-progress driver circuit based on an ATmega32U4 AVR under electronics/splitflap.pro (KiCad project) which is under very active development. The driver supports 4 stepper motors using ULN2003 darlington arrays (which you easily remove from the 28byj-48 driver boards that often come with the motors) and 4 optical home position inputs (for GP2S60 IR reflectance sensors), with a micro-USB connector for computer control.

The PCB layout is designed to fit within the 5cm x 5cm bounds for a number of low-cost PCB manufacturers (e.g. Seeed Studio), and can be populated in two separate configurations (since many low-cost PCB manufacturers have a minimum order of identical PCBs):
- As a 4-channel driver board, with ATmega32U4, 3x ULN2003, USB, etc
- As a home sensor board for a single character, with GP2S60 IR reflectance sensor and 3-pin connector
This way, with an order of 5 identical PCBs you can populate a single 4-channel driver board and four home sensor boards for a complete electronics set for 4 split-flap units.
These are automatically updated on every commit with the latest rendering from the master branch. See this blog post for more details on how that works: Automated KiCad, OpenSCAD rendering using Travis CI.
Latest (experimental!) PCB Gerbers: zip
Latest (experimental!) PCB Packet: pdf
Latest (experimental!) rough bill of materials: csv
The PCB layout can be rendered to an svg or png (seen above) by running electronics/generate_svg.py. This uses KiCad's python scripting API to render several layers to individual svg files, manipulates them to apply color and opacity settings, and then merges them to a single svg. For additional details, see this blog post: Scripting KiCad Pcbnew exports.
For reviewing the design, a pdf packet with copper, silkscreen, and drill info can be produced by running electronics/generate_pdf.py.
Gerber files for fabrication can be exported by running electronics/generate_gerber.py. This generates gerber files and an Excellon drill file with Seeed Studio's naming conventions and produces a .zip which can be sent for fabrication.
EESchema isn't easily scriptable, so to export the schematic and bill of materials electronics/scripts/export_schematic.py and export_bom.py start an X Virtual Frame Buffer (Xvfb) and open the eeschema GUI within that virtual display, and then send a series of hardcoded key presses via xdotool to interact with the GUI and click through the dialogs. This is very fragile but seems to work ok for now. For additional details, see this blog post: Using UI automation to export KiCad schematics.
The driver firmware is written using Arduino (superficially targeting the Arduino Micro board, since it's based on the same ATmega32U4 chip used in this design) and is available at arduino/splitflap/splitflap.ino. To avoid the need for an ICSP programmer (since Arduino doesn't support the stock DFU bootloader on the ATMega32U4), you can use Arduino only to compile the program (Sketch -> Export compiled binary) and then install the .hex binary onto the AVR separately using the dfu-programmer tool.
The firmware currently runs a basic closed-loop controller that accepts letters over USB serial and drives the stepper motors using a runtime-computed acceleration ramp for smooth control. The firmware automatically calibrates the spool position at startup, using the IR reflectance sensor, and will automatically recalibrate itself if it ever detects that the spool position has gotten out of sync. If a commanded rotation is expected to bring the spool past the "home" position, it will confirm that the sensor is triggered neither too early nor too late; otherwise it will search for the "home" position to get in sync before continuing to the desired letter.
There is currently no example computer software demonstrating how to communicate with the driver firmware over USB. This is planned for the future, but the protocol is currently undocumented and likely to change as the firmware continues to be developed. In the meantime, the best "documentation" of the protocol is the firmware source code itself.
I'd love to hear your thoughts and questions about this project, and happy to incorporate any feedback you might have into these designs! Please feel free (and encouraged) to open GitHub issues, email me directly, reach out on Twitter, and get involved in the open source development and let's keep chatting and building together!
The vast majority of this project is licensed under Apache v2 (see LICENSE.txt for full details).
Copyright 2015-2016 Scott Bezek and the splitflap contributors
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
limitations under the License.



