Evaluating generating series with large input data using Map-Reduce pattern
- Live Demo: http://generatingseries.herokuapp.com
Parallel programming allows the program to run multiple processes asynchronously. This allows a large data set to be split into smaller inputs distributed to each worker node.
This programming technique can be useful for evaluating the sum of generating series (defined in the next section). An example below shows how to compute a generating series with a weight function that returns 1 if the input is consonant, and 0 if it is a vowel.
Instead of evaluating every term, we can first collect the like terms, evaluate the sum of coefficients, then evaluate the combined term. List comprehension in Python is highly optimized for collecting particular sublist of elements from a list. We can, thus, use Python list comprehension to collect the like terms.
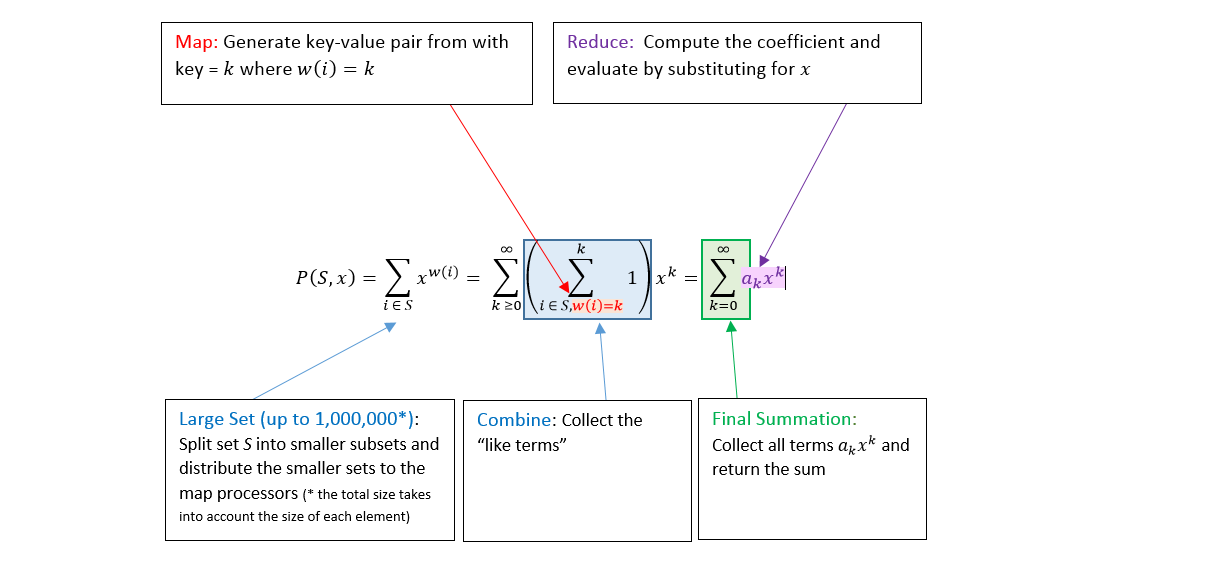
Each map node computes one segment of the input data, a sublist of elements. Map node produces (or emits) key-value pairs for every element in the list, each corresponding to a particular term in the generating series.
A power of each term is determined by a function of one element in the list, and the powers of x serve as keys when combining like terms.
Combiner aggregates like terms with the same power (same keys). Reduce node then computes the value of the combined term. Finally, the total sum is determined by aggregating the outputs of each reduce node.
Generating Series is defined by the generating function P(S,x)
- v stores the upper and lower bound for keys see compute_local.py for detailed documentation
Python 3
The optimization is implemented in five steps:
Optimizations
- Step 1. Map Reduce Pattern
Map reduce pattern is used to take advantages of multiprocessing capabilities of the machine.
- Step 2. Local Combiner as opposed to Global Combiner
Instead of combining outputs of all map nodes, designate a local combiner to each map node.
- Step 3. Adjustment in number of map nodes
- Step 4. Quick way to determine upper and lower bound for key
Keep track of maximum and minimum key in the past outputs. This is to prevent going over the list multiple times to determine maximum and minimum keys.
- Step 5. Increase the number of reduce nodes to speed up reduce processes
- First Step: Split input data into smaller inputs and follow Map Reduce Pattern

- Up to Step 4 (compute_local_optimized_step_4.py): Local Combine

- Up to Step 5 (compute_local.py): Splits Reduce Nodes further to increase number of parallel reduce processes

- Customize client.py
-
weight function w() :
-
... returns an int or float, a power of x
-
get_num_map_nodes(size_param: integer) optional:
-
... returns number of map nodes where size_param is a variable you can use to categorize input by size
-
x():
-
... returns a number to be used to substitute for variable x
-
create_list():
-
... returns a list to be used as an input
- Run command [your_path_to]/Python34/python.exe compute_local.py
- Call function compute(lst,size_param,option)
- ... where lst is a list of (list, integer, or float)
- size_param is a variable that indicates the size of the input (you define it in anyway you like)
- option is one of 'fixed' or 'not_fixed'
- 'fixed' : set number of map nodes to 5 (you can modify this in compute_local.py)
- 'not_fixed' : set number of map nodes to get_num_map_nodes(size_param) in client.py
-
You can also run different tests by uncommenting some of the codes in name == main at the bottom of compute_local.py source code. See compute_local.py for details.
-
Recommendation
If unsure, it is recommended to set size_param = len().
It is also recommended to set option to not_fixed to minimize running time while 'fixed' option is recommended for testing purposes