数据科学家
https://github.com/ClimbsRocks
https://github.com/rhiever
https://github.com/loliverhennigh
- Art Generation
- Image Classifier
- Earthquake Prediction
- Language Translation
- Linear Regression
- Music Generation
- Sentiment Analysis
- Text Based Chatbot
https://www.cs.waikato.ac.nz/ml/weka/ java api frameworks https://github.com/ivan-vasilev/neuralnetworks java 库 https://software.intel.com/zh-cn/ai-academy/students/kits intel ml 教程 http://neuralnetworksanddeeplearning.com/index.html 基础
code to accompany blog posts
tensorflow 基础
-
Transfer learning from multiple pre-trained computer vision models In this short blog post I describe the (somewhat under-utilized) method of combining multiple pre-trained cv models using stacking, to enhance classification results on a new dataset.
-
Go with the Flow: Up and Running with TensorFlow
-
Understanding TensorFlow Basics
-
Convolutional Neural Networks
-
Text I: Working with Text and Sequences, and TensorBoard Visualization.
-
Text II: Word Vectors, Advanced RNN, and Embedding Visualization.
-
TensorFlow Abstractions and Simplications.
-
Queues, Threads, and Reading Data.
-
Distributed TensorFlow.
-
Exporting and Serving Models with TensorFlow.
Check out the associated repo from our OSCON2017 training.
If you like the book, please rate it on Amazon :)
-
Densely Connected Convolutional Network implemented in the DenseNet folder
-
Visualizing and Understanding Convolutional Networks implemented in the DeconvNet folder
-
Improving Stochastic Gradient Descent With Feedback implemented in the Eve folder
-
Colorful Image Colorization implemented in the Colorful folder
-
Deep Feature Interpolation for Image Content Changes implemented in the DFI folder
-
Several Generative Adversarial Networks (GAN) models and techniques in the GAN folder
-
pix2pix in the pix2pix folder
-
InfoGAN in the InfoGAN folder
-
WassersteinGAN in the WassersteinGAN folder and WGAN-GP folder for a tensorflow implementation.
-
BEGAN in the BEGAN folder
-
Scaling the Scattering Transform: Deep Hybrid Networks in the ScatteringTransform folder
2018 论文复现赛 要了解文中提到的复现赛详情,看这里:http://www.cs.mcgill.ca/~jpineau/ICLR2018-ReproducibilityChallenge.html
<自然》对1500名科学家的调查:http://www.nature.com/news/1-500-scientists-lift-the-lid-on-reproducibility-1.19970?WT.mc_id=FBK_NatureNews
ICML2017论文ReproducibilityinMachineLearning-BasedStudies:AnExampleofTextMining:https://openreview.net/pdf?id=By4l2PbQ-
QZ报道:https://qz.com/1118671/the-titans-of-ai-are-getting-their-work-double-checked-by-students/
论文
DSLR-QualityPhotosonMobileDeviceswithDeepConvolutionalNetworks StackGAN:TexttoPhoto-realisticImageSynthesiswithStackedGenerativeAdversarialNetworks High-QualityCorrespondenceandSegmentationEstimationforDual-LensSmart-PhonePortraits PhotographicImageSynthesiswithCascadedRefinementNetworks FoveaNet:Perspective-awareUrbanSceneParsing ArbitraryStyleTransferinReal-timewithAdaptiveInstanceNormalization Dense-CaptioningEventsinVideos TowardsDiverseandNaturalImageDescriptionsviaaConditionalGAN Weakly-supervisedlearningofvisualrelations InferringandExecutingProgramsforVisualReasoning TurningCornersintoCameras:PrinciplesandMethods GeneratingHigh-QualityCrowdDensityMapsusingContextualPyramidCNNs DeepRoadMapper:ExtractingRoadTopologyfromAerialImages
https://pair-code.github.io/facets/可嵌入到jupyter notebook 的数据可视化工具 代码:https://github.com/PAIR-code/facets
语音识别工具:https://github.com/kaldi-asr/kaldi
示例:https://github.com/kaldi-asr/kaldi/tree/master/egs/ami/s5/local/tfrnnlm
https://github.com/DeepScale/SqueezeNet 两个小的模型的输出特征拼在一起,然后再进行分配,拼成一个大模型。然后还可以增加Batchnorm、dropout、L2 我们发现ResNet效果是最好的,DenseNet效果紧随其后。VGG,Inceptionv3效果差一点。最差的是AlexNet和SqueezeNet 不同的模型集成手段,比如平均Bagging,BaggingEnsembleSelection,还有AttentionStacking,AttentionStacking是我们自己加入的一个东西,效果还不错。
http://www.sohu.com/a/163567410_114877
http://deepcognition.ai/ 深度学习云,速度挺快
tensorflow eager 版本 使得图形化编程即时化 可读性更强 谷歌研究博客地址:https://research.googleblog.com/2017/10/eager-execution-imperative-define-by.html
GitHub代码地址:https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow/blob/master/tensorflow/contrib/eager/README.md代码
使用手册:https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow/blob/master/tensorflow/contrib/eager/python/g3doc/guide.md
Anh Nguyen的论文《Deep Neural Networks are Easily Fooled: High Confidence Predictions for Unrecognizable Images》
http://nbviewer.jupyter.org/github/BVLC/caffe/blob/master/examples/00-classification.ipynb
https://github.com/yosinski/deep-visualization-toolbox
见于Christian Szegedy的论文《Intriguing properties of neural networks 》
Understanding Deep Image Representations by Inverting Them
A Neural Algorithm of Artistic Style
至于Gram矩阵为什么能作为重建风格的依据,论文《Demystifying Neural Style Transfer》 https://github.com/yosinski/deep-visualization-toolbox
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/27343585
https://github.com/devnag/pytorch-generative-adversarial-networks
https://github.com/mokemokechicken/keras_np i http://blog.csdn.net/sinat_33761963/article/details/53521206
tensorflow框架下有一个序列到序列进行翻译的学习案例。 文档可以参见https://www.tensorflow.org/versions/r0.11/tutorials/seq2seq/index.html 代码可以参见https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow/tree/master/tensorflow/models/rnn/translate
生成字符级别的语言模型 上一个笔记中将的语言生成模型是针对word来做的,这里的原理是完全一样的,只是针对chart来做。将所有chart,包括标点符号全部作为输入。大致的结构如下:
![QQ截图20161027132426.png-71.6kB][131]
这个案例的代码可以见:https://gist.github.com/karpathy/d4dee566867f8291f086
来看一下模型在学习过程中的进展是如何的: 学习第100轮的时候,还很混乱 QQ截图20161027132843.png-14.7kB
学习第300轮之后,已经能正确得插入词与词之间的空格 QQ截图20161027132851.png-20.2kB
第500轮之后,知道了要加句号在某个位置,并且句号之后加一个空格 QQ截图20161027132858.png-14.7kB
700-900轮时,已经非常像英文的句子,已经学会了使用引号,省略号等,学出来的词也已经是标准的英文单词 QQ截图20161027132905.png-11.4kB
1200轮的时候,能识别人名要大写,并且单词和句子也几乎是正确的。 QQ截图20161027132912.png-21.7kB
所以,RNN与学习的时候是一个逐步学习的过程。
3.2 生成维基百科 同样的原理,如果喂给RNN的是维基百科的内容,那么它也能在学习之后模仿写出维基百科。 已经有小伙伴整理了一部分维基百科的数据做成text的格式,有兴趣的小伙伴可以去下载数据测试一下。 数据地址:http://cs.stanford.edu/people/karpathy/char-rnn/wiki.txt
3.3 生成模型写食谱 同样,RNN也可以去模仿写食谱。这个案例的具体信息见以下链接。 案例:https://gist.github.com/nylki/1efbaa36635956d35bcc 代码:https://gist.github.com/karpathy/d4dee566867f8291f086 数据:http://www.ffts.com/recipes/lg/lg32965.zip
3.4 生成模型写奥巴马演讲稿 还有一些小伙伴尝试了用RNN去写奥巴马的演讲稿。 数据下载地址: https://medium.com/@samim/obama-rnn-machine-generated-political-speeches-c8abd18a2ea0#.9sb793kbm
3.5 合成音乐 音乐也是一个时序的一个任务。将乐谱用一种方式表示出来输入RNN,预测完之后,再把它转换成音符。 具体的过程请见blog:https://highnoongmt.wordpress.com/2015/05/22/lisls-stis-recurrent-neural-networks-for-folk-music-generation/
还有一个更高级的合成音乐案例,这里面还涉及到了乐理的一些知识, 具体请看blog:http://www.hexahedria.com/2015/08/03/composing-music-with-recurrent-neural-networks/
[13lqh7xlyv2owk5rw4fyslus2d/QQ%E6%88%AA%E5%9B%BE20161027145714.png
目前正在进行更复杂的内存结构的趋势。端到端内存网络允许网络在输出之前读取相同的输入序列多次,在每一步更新内存内容。例如,通过对输入的故事进行多个推理步骤来回答问题
在未来,我们可能会看到记忆和注意力机制之间的更清晰的区别,也许是沿着强化学习神经图灵机的路线,它试图学习访问模式来处理外部接口。
http://deeplearning.cs.cmu.edu/ 课程
https://github.com/dennybritz/deeplearning-papernotes 重要论文汇总
https://github.com/rockingdingo/deepnlp
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/40601552/visualizing-attention-activation-in-tensorflow
神经网络已经可以有效率的解决不同的问题,但是,即便仅仅对图片分类任务来说,设计他们的结构需要有能力的,我们的目标是最小化人类的参与度,所以我们使用进化算法来自动发现神经网络. 尽管需要显著的计算要求,我们展示了使用进化模型对去年发布的一些模型提高的精度。特别是,我们使用这个技术在cifar-10 和cifar-100数据集上进行史无前例的发现模型。
该Repo内容为知乎专栏《机器不学习》的源代码。
专栏地址:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/zhaoyeyu
TensorFlow
基于RNN(LSTM)对《安娜卡列尼娜》英文文本的学习,实现一个字符级别的生成器。
实现skip-gram算法的Word2Vec,基于对英文语料的训练,模型学的各个单词的嵌入向量。
基于RNN实现歌词生成器。
基于RNN Encoder-Decoder结构的Seq2Seq模型,实现对一个单词中字母的排序。
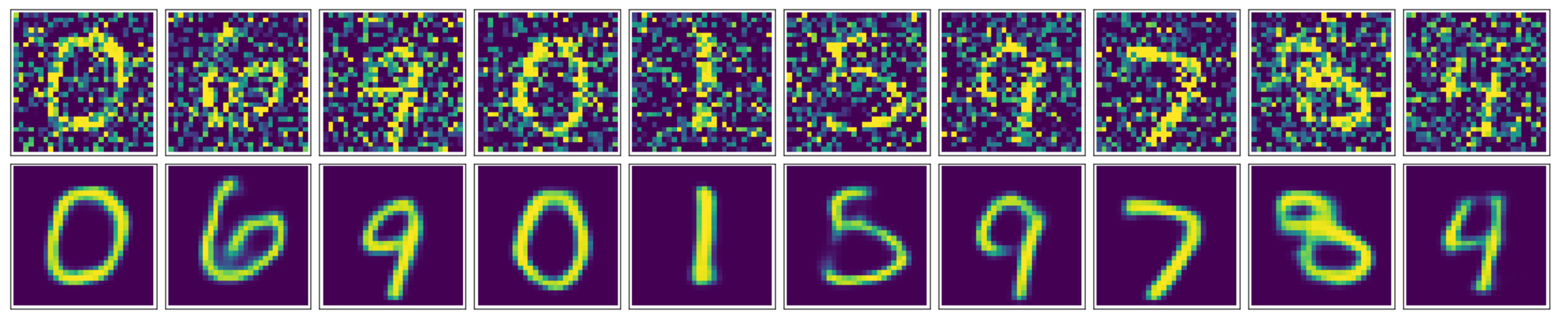
基于MNIST手写数据集训练了一个自编码器,并在此基础上增加卷积层实现一个卷积自编码器,从而实现对图像的降噪。
文章地址:利用卷积自编码器对图片进行降噪
对Kaggle上CIFAR图像分类比赛的一个实现,分别对比了KNN和卷积神经网络在数据上的表现效果。
文章地址:利用卷积神经网络处理CIFAR图像分类
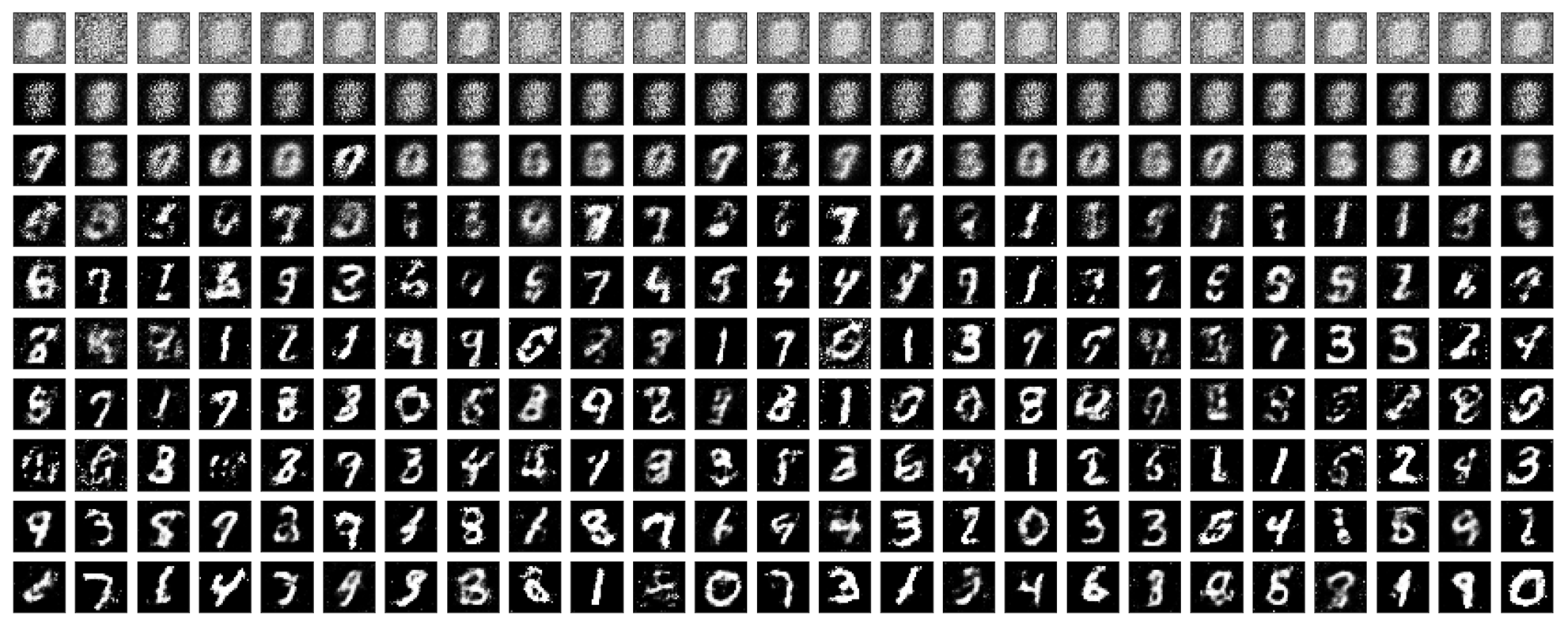
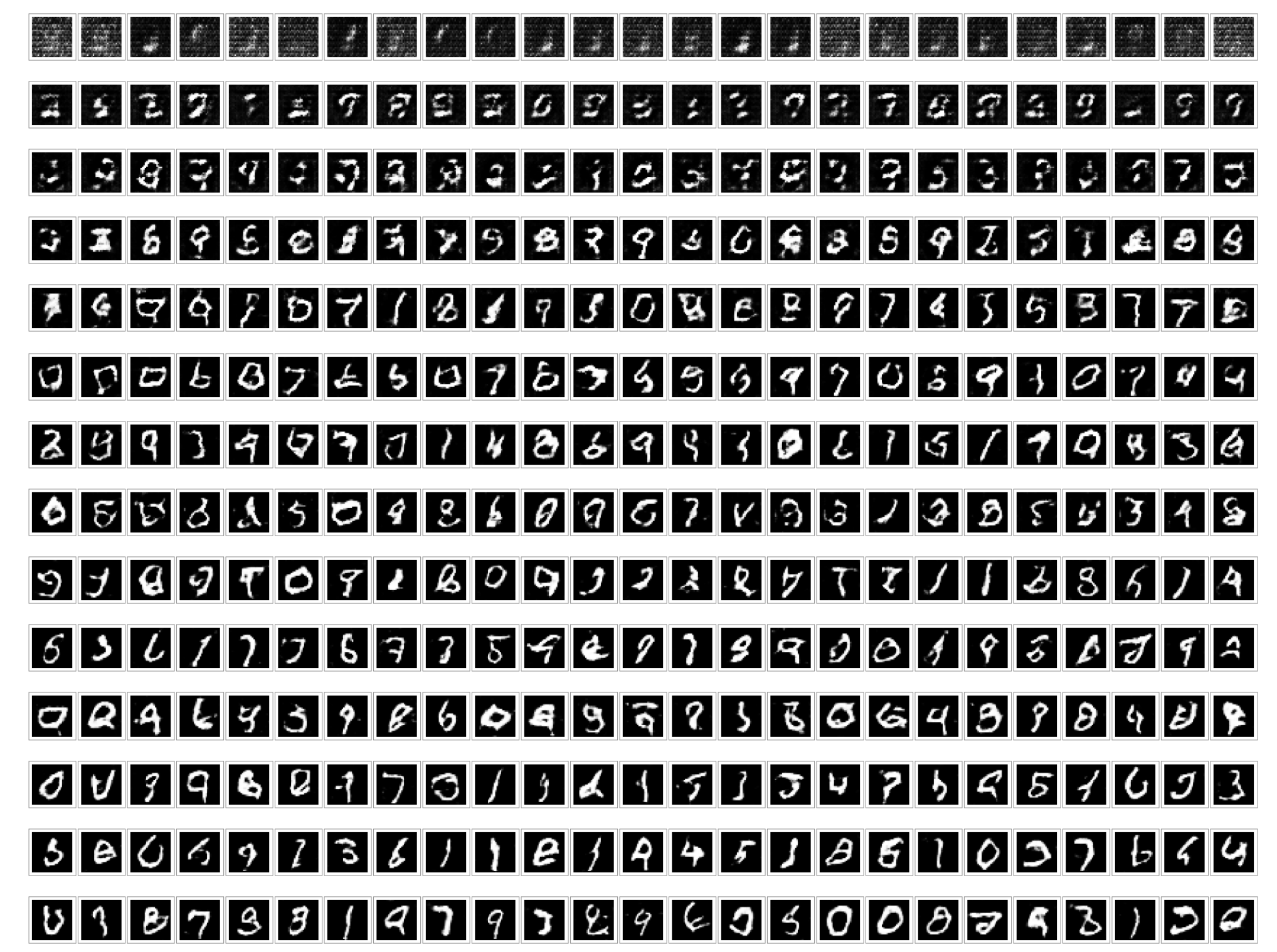
基于MNIST手写数据集,训练了一个隐层为Leaky ReLU的生成对抗网络,让模型学会自己生成手写数字。
基于MNIST数据集训练了一个DCGAN,加入了Batch normalization,加速模型收敛并提升新能。
文章地址:深度卷积GAN之图像生成
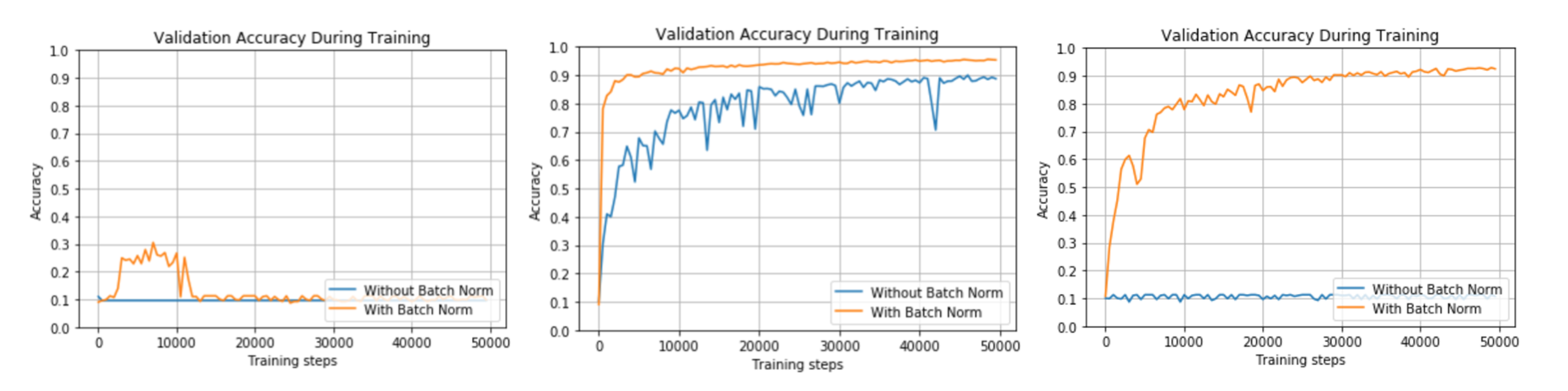
该部分代码基于MNIST手写数据集构造了一个三层的全连接层神经网络。通过改变不同参数来测试BN对于模型性能的影响。同时利用TensorFlow实现底层的batch normalization。
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
from collections import Counter
from sklearn.datasets import fetch_20newsgroupsimport tensorflow as tf
my_graph = tf.Graph()
with tf.Session(graph=my_graph) as sess:
x = tf.constant([1,3,6])
y = tf.constant([1,1,1])
op = tf.add(x,y)
result = sess.run(fetches=op)
print(result)[2 4 7]
vocab = Counter()
text = "Hi from Brazil"
for word in text.split(' '):
word_lowercase = word.lower()
vocab[word_lowercase]+=1
def get_word_2_index(vocab):
word2index = {}
for i,word in enumerate(vocab):
word2index[word] = i
return word2indexword2index = get_word_2_index(vocab)
total_words = len(vocab)
matrix = np.zeros((total_words),dtype=float)
for word in text.split():
matrix[word2index[word.lower()]] += 1
print("Hi from Brazil:", matrix)Hi from Brazil: [ 1. 1. 1.]
matrix = np.zeros((total_words),dtype=float)
text = "Hi"
for word in text.split():
matrix[word2index[word.lower()]] += 1
print("Hi:", matrix)Hi: [ 1. 0. 0.]
categories = ["comp.graphics","sci.space","rec.sport.baseball"]
newsgroups_train = fetch_20newsgroups(subset='train', categories=categories)
newsgroups_test = fetch_20newsgroups(subset='test', categories=categories)print('total texts in train:',len(newsgroups_train.data))
print('total texts in test:',len(newsgroups_test.data))total texts in train: 1774
total texts in test: 1180
print('text',newsgroups_train.data[0])
print('category:',newsgroups_train.target[0])text From: jk87377@lehtori.cc.tut.fi (Kouhia Juhana)
Subject: Re: More gray levels out of the screen
Organization: Tampere University of Technology
Lines: 21
Distribution: inet
NNTP-Posting-Host: cc.tut.fi
In article <1993Apr6.011605.909@cis.uab.edu> sloan@cis.uab.edu
(Kenneth Sloan) writes:
>
>Why didn't you create 8 grey-level images, and display them for
>1,2,4,8,16,32,64,128... time slices?
By '8 grey level images' you mean 8 items of 1bit images?
It does work(!), but it doesn't work if you have more than 1bit
in your screen and if the screen intensity is non-linear.
With 2 bit per pixel; there could be 1*c_1 + 4*c_2 timing,
this gives 16 levels, but they are linear if screen intensity is
linear.
With 1*c_1 + 2*c_2 it works, but we have to find the best
compinations -- there's 10 levels, but 16 choises; best 10 must be
chosen. Different compinations for the same level, varies a bit, but
the levels keeps their order.
Readers should verify what I wrote... :-)
Juhana Kouhia
category: 0
vocab = Counter()
for text in newsgroups_train.data:
for word in text.split(' '):
vocab[word.lower()]+=1
for text in newsgroups_test.data:
for word in text.split(' '):
vocab[word.lower()]+=1print("Total words:",len(vocab))Total words: 119930
total_words = len(vocab)
def get_word_2_index(vocab):
word2index = {}
for i,word in enumerate(vocab):
word2index[word.lower()] = i
return word2index
word2index = get_word_2_index(vocab)
print("Index of the word 'the':",word2index['the'])Index of the word 'the': 10
def get_batch(df,i,batch_size):
batches = []
results = []
texts = df.data[i*batch_size:i*batch_size+batch_size]
categories = df.target[i*batch_size:i*batch_size+batch_size]
for text in texts:
layer = np.zeros(total_words,dtype=float)
for word in text.split(' '):
layer[word2index[word.lower()]] += 1
batches.append(layer)
for category in categories:
y = np.zeros((3),dtype=float)
if category == 0:
y[0] = 1.
elif category == 1:
y[1] = 1.
else:
y[2] = 1.
results.append(y)
return np.array(batches),np.array(results)print("Each batch has 100 texts and each matrix has 119930 elements (words):",get_batch(newsgroups_train,1,100)[0].shape)Each batch has 100 texts and each matrix has 119930 elements (words): (100, 119930)
print("Each batch has 100 labels and each matrix has 3 elements (3 categories):",get_batch(newsgroups_train,1,100)[1].shape)Each batch has 100 labels and each matrix has 3 elements (3 categories): (100, 3)
# Parameters
learning_rate = 0.01
training_epochs = 10
batch_size = 150
display_step = 1
# Network Parameters
n_hidden_1 = 100 # 1st layer number of features
n_hidden_2 = 100 # 2nd layer number of features
n_input = total_words # Words in vocab
n_classes = 3 # Categories: graphics, sci.space and baseball
input_tensor = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None, n_input],name="input")
output_tensor = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None, n_classes],name="output") def multilayer_perceptron(input_tensor, weights, biases):
layer_1_multiplication = tf.matmul(input_tensor, weights['h1'])
layer_1_addition = tf.add(layer_1_multiplication, biases['b1'])
layer_1 = tf.nn.relu(layer_1_addition)
# Hidden layer with RELU activation
layer_2_multiplication = tf.matmul(layer_1, weights['h2'])
layer_2_addition = tf.add(layer_2_multiplication, biases['b2'])
layer_2 = tf.nn.relu(layer_2_addition)
# Output layer
out_layer_multiplication = tf.matmul(layer_2, weights['out'])
out_layer_addition = out_layer_multiplication + biases['out']
return out_layer_addition# Store layers weight & bias
weights = {
'h1': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_input, n_hidden_1])),
'h2': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_hidden_1, n_hidden_2])),
'out': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_hidden_2, n_classes]))
}
biases = {
'b1': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_hidden_1])),
'b2': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_hidden_2])),
'out': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_classes]))
}
# Construct model
prediction = multilayer_perceptron(input_tensor, weights, biases)
# Define loss and optimizer
loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=prediction, labels=output_tensor))
optimizer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate=learning_rate).minimize(loss)
# Initializing the variables
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()# Launch the graph
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(init)
# Training cycle
for epoch in range(training_epochs):
avg_cost = 0.
total_batch = int(len(newsgroups_train.data)/batch_size)
# Loop over all batches
for i in range(total_batch):
batch_x,batch_y = get_batch(newsgroups_train,i,batch_size)
# Run optimization op (backprop) and cost op (to get loss value)
c,_ = sess.run([loss,optimizer], feed_dict={input_tensor: batch_x,output_tensor:batch_y})
# Compute average loss
avg_cost += c / total_batch
# Display logs per epoch step
if epoch % display_step == 0:
print("Epoch:", '%04d' % (epoch+1), "loss=", \
"{:.9f}".format(avg_cost))
print("Optimization Finished!")
# Test model
correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(prediction, 1), tf.argmax(output_tensor, 1))
# Calculate accuracy
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, "float"))
total_test_data = len(newsgroups_test.target)
batch_x_test,batch_y_test = get_batch(newsgroups_test,0,total_test_data)
print("Accuracy:", accuracy.eval({input_tensor: batch_x_test, output_tensor: batch_y_test}))Epoch: 0001 loss= 1133.908114347
Epoch: 0002 loss= 329.093700409
Epoch: 0003 loss= 111.876660109
Epoch: 0004 loss= 72.552971845
Epoch: 0005 loss= 16.673050320
Epoch: 0006 loss= 16.481995190
Epoch: 0007 loss= 4.848220565
Epoch: 0008 loss= 0.759822878
Epoch: 0009 loss= 0.000000000
Epoch: 0010 loss= 0.079848485
Optimization Finished!
Accuracy: 0.75
- Background Materials
- Machine Learning Basics
- Concepts, Capacity, Estimators, Linear Regression
- MLE, Bayesian, Other ML Algorithms
- Stochastic Gradient Descent, etc
- Deep Neural Networks
- Regularization
- Optimization
- Convolutional Neural Networks
- Embeddings
- Recurrent Neural Networks, LSTM, GRU
Tensorflow (tf) Experiments
- Hello World!
- Linear Algebra
- Matrix Decomposition
- Probability Distributions using TensorBoard
- Linear Regression by PseudoInverse
- Linear Regression by Gradient Descent
- Under Fitting in Linear Regression
- Optimal Fitting in Linear Regression
- Over Fitting in Linear Regression
- Nearest Neighbor
- Principal Component Analysis
- Logical Ops by a 2-layer NN (MSE)
- Logical Ops by a 2-layer NN (Cross Entropy)
- NotMNIST Deep Feedforward Network: Code for NN and Code for Pickle
- NotMNIST CNN
- word2vec
- Word Prediction/Story Generation using LSTM. Belling the Cat by Aesop Sample Text Story